Optimal RANSAC Method for Segmentation of Complex Building Roof Planes
-
摘要:
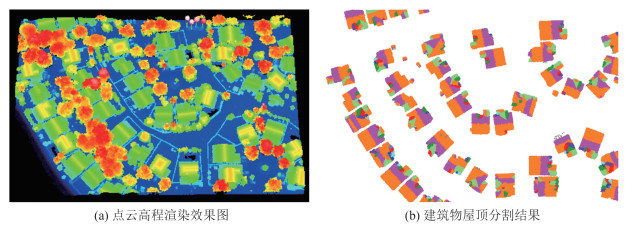
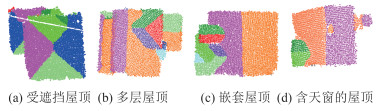
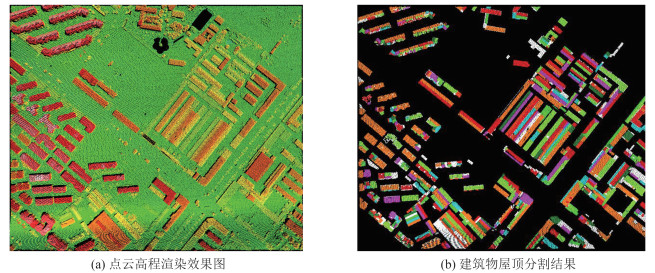
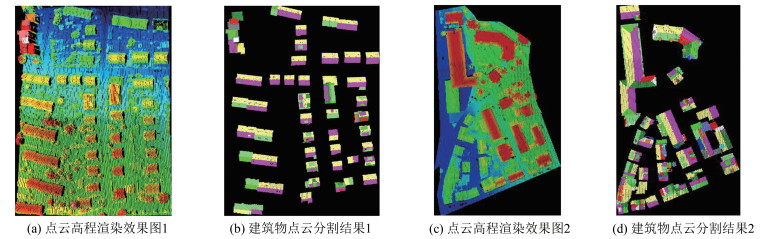
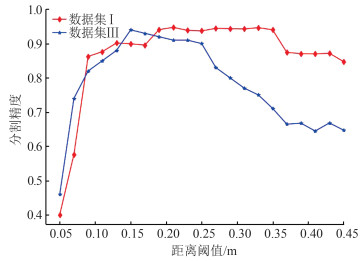
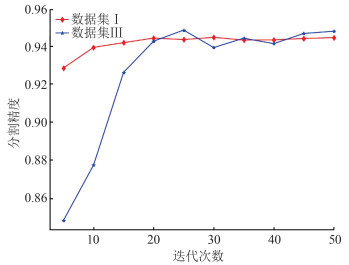
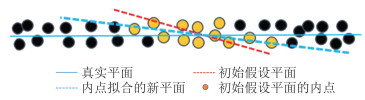
针对传统随机采样一致性(random sample consensus,RANSAC)算法对复杂屋顶的分割缺陷,提出一种复杂屋顶平面的RANSAC优化分割方法。首先,在点云法向量估计的基础上,利用点法式方程优化种子点选取过程,提高初始平面选择的有效性;然后,采用距离与法向加权法抑制虚假平面生成,并利用加权函数进行平面内点的迭代修正,提高面片分割的准确性;最后,利用面片竞争方法优化分割结果,实现屋顶点云的分割处理。多组点云分割实验结果表明,该方法能有效抑制虚假平面,对复杂建筑物的屋顶平面分割结果的精确率、召回率和整体精度分别达到96.8%、98.2%和95.1%。相比传统方法,该方法在点云分割结果正确率及耗时方面均有明显优势。
Abstract:ObjectivesAiming at the defects of the traditional random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm for complex roof segmentation, is paper proposes an optimal RANSAC method for segmentation of complex building roof planes.
MethodsFirst, the normal vector of the point cloud is estimated based on the k-nearest neighbor of the point cloud, and the seed selection process is optimized by using the point normal equation to improve the effectiveness of the initial plane generation; Second, the weight function based on the point normal and its distance to the initial plane is used to suppress the false plane generation. And inner points of the plane are modified iteratively by the weight function to improve the correctness of the segmented plane. Finally, the patch competition method is used to optimize the segmentation results and achieve roof point cloud segmentation.
ResultsSegmentation experiments results of multiple groups of buildings show that the proposed method can effectively suppress false plane, and the precision, recall and overall accuracy of roof plane segmentation of complex buildings are 96.8%, 98.2% and 95.1% respectively.
ConclusionsCompared with the traditional method, the proposed method has obvious advantages in the accuracy and time-consuming of point cloud segmentation results.
-
-
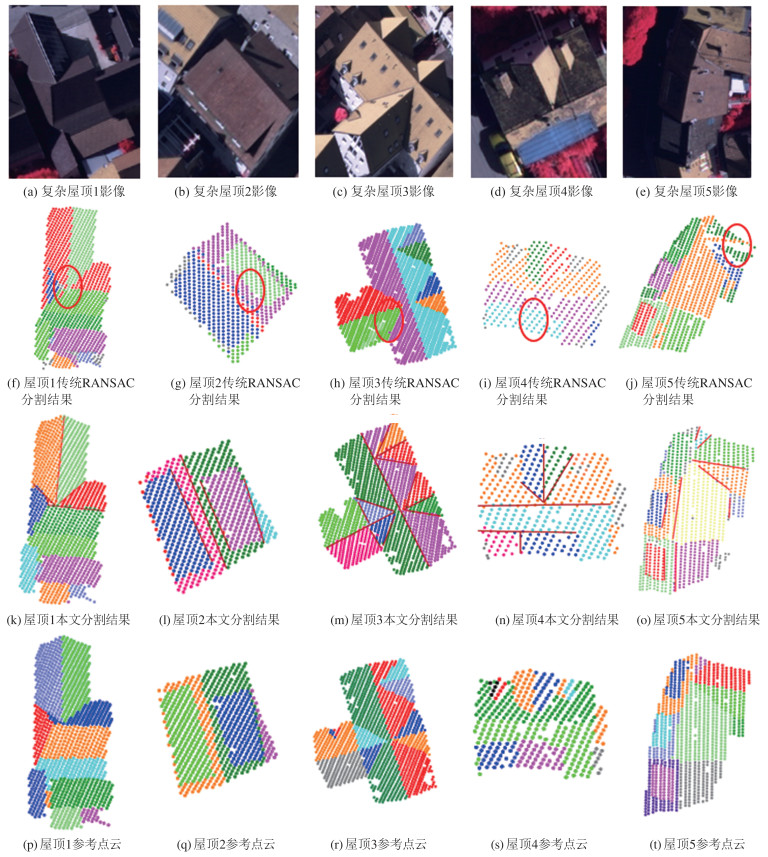
表 1 复杂屋顶点云分割性能对比
Table 1 Performance Comparison of Complex Roof Point Cloud Segmentation
屋顶序号 传统RANSAC方法 本文方法 P R TOA 耗时/s P R TOA 耗时/s 1 0.948 0.908 0.865 3.45 0.989 0.991 0.980 1.31 2 0.923 0.853 0.784 1.64 0.997 0.990 0.987 0.63 3 0.970 0.969 0.937 4.73 0.989 0.996 0.985 1.42 4 0.963 0.928 0.896 1.09 0.979 0.969 0.950 0.38 5 0.847 0.842 0.731 2.79 0.983 0.967 0.952 1.81 表 2 数据集Ⅱ屋顶点云分割精度对比
Table 2 Performance Comparison of Roof Point Cloud in Dataset Ⅱ
方法 P R TOA I-RANSAC 0.885 0.904 0.809 OD-RANSAC 0.841 0.943 0.765 本文方法 0.968 0.982 0.951 -
[1] Yu D, Ji S, Liu J, et al. Automatic 3D Building Reconstruction from Multi-view Aerial Images with Deep Learning[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021, 171: 155-170. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.11.011
[2] 黄荣刚, 杨必胜, 李健平, 等. 利用目标区域拓扑关系图提取建筑物点云[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2017, 42(4): 475-481. Huang Ronggang, Yang Bisheng, Li Jianping, et al. Building Points Detection from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds Using Topological Relationship Graph Within Each Object Region[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(4): 475-481.
[3] 文学东, 陈为民, 谢洪, 等. 一种融合多源特征的建筑物三维模型重建方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(5): 731-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201905014.htm Wen Xuedong, Chen Weimin, Xie Hong, et al. A Method for Building Model Reconstruction Based on Multi⁃source Feature Fusion[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(5): 731-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201905014.htm
[4] Zhao C, Guo H T, Lu J, et al. A New Approach for Roof Segmentation from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 12(4): 377-386. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2020.1847348
[5] Xu Y, Yao W, Hoegner L, et al. Segmentation of Building Roofs from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds Using Robust Voxel-Based Region Growing[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 8(11): 1062-1071. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2017.1349961
[6] 赵瑞斌, 庞明勇, 张燕玲, 等. 机载LiDAR点云中精细建筑物顶面的渐进提取[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2017, 29(4): 624-631. Zhao Ruibin, Pang Mingyong, Zhang Yanling, et al. Progressively Extracting Accurate Building Roofs from Airborne LiDAR Data[J]. Journal of Computer‐Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2017, 29(4): 624-631.
[7] Li Z, Shan J. RANSAC-Based Multi Primitive Building Reconstruction from 3D Point Clouds[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 185: 247-260. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.12.012
[8] Wang X S, Chan T O, Liu K, et al. A Robust Segmentation Framework for Closely Packed Buildings from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(14): 5147-5165. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1727053
[9] Albano R. Investigation on Roof Segmentation for 3D Building Reconstruction from Aerial LiDAR Point Clouds[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(21): 4674. doi: 10.3390/app9214674
[10] Cao R J, Zhang Y J, Liu X Y, et al. Roof Plane Extraction from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 38(12): 3684-3703. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2017.1302112
[11] Demir N. Automated Detection of 3D Roof Planes from LiDAR Data[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2018, 46(8): 1265-1272. doi: 10.1007/s12524-018-0802-2
[12] Dal P A P, Yano M S. Ransac-Based Segmentation for Building Roof Face Detection in LiDAR Point Cloud[C]// IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018.
[13] Dehbi Y, Henn A, Gröger G, et al. Robust and Fast Reconstruction of Complex Roofs with Active Sampling from 3D Point Clouds[J]. Transactions in GIS, 2021, 25(1): 112-133. doi: 10.1111/tgis.12659
[14] Yi Z, Wang H, Duan G, et al. An Airborne LiDAR Building-Extraction Method Based on the Naive Bayes-RANSAC Method for Proportional Segmentation of Quantitative Features[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2021, 49(2): 393-404. doi: 10.1007/s12524-020-01222-4
[15] Canaz Sevgen S, Karsli F. An Improved RANSAC Algorithm for Extracting Roof Planes from Airborne Lidar Data[J]. The Photogrammetric Record, 2020, 35(169): 40-57. doi: 10.1111/phor.12296
[16] Dey E K, Awrangjeb M, Stantic B. Outlier Detection and Robust Plane Fitting for Building Roof Extraction from LiDAR Data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(16): 6325-6354.
[17] Xu B, Jiang W S, Shan J, et al. Investigation on the Weighted RANSAC Approaches for Building Roof Plane Segmentation from LiDAR Point Clouds[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(1): 5. doi: 10.3390/rs8010005





 下载:
下载: