-
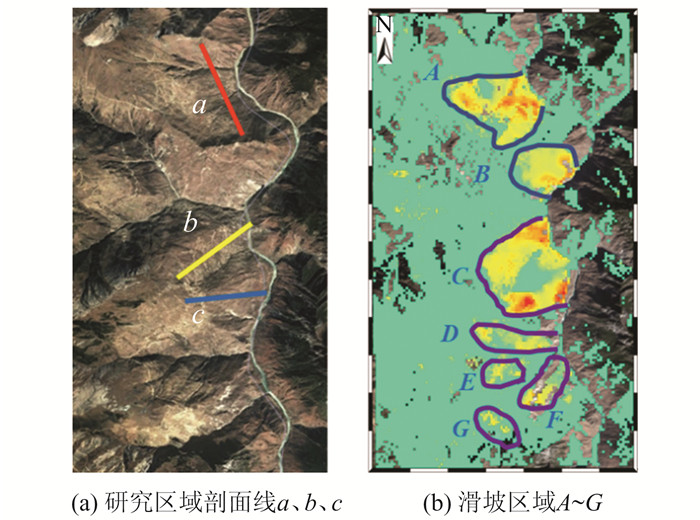
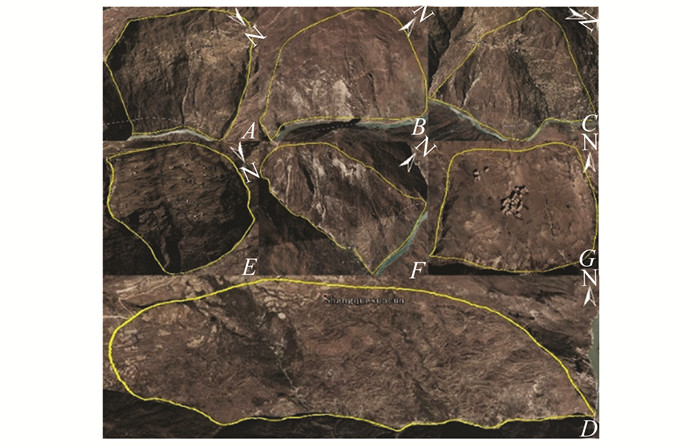
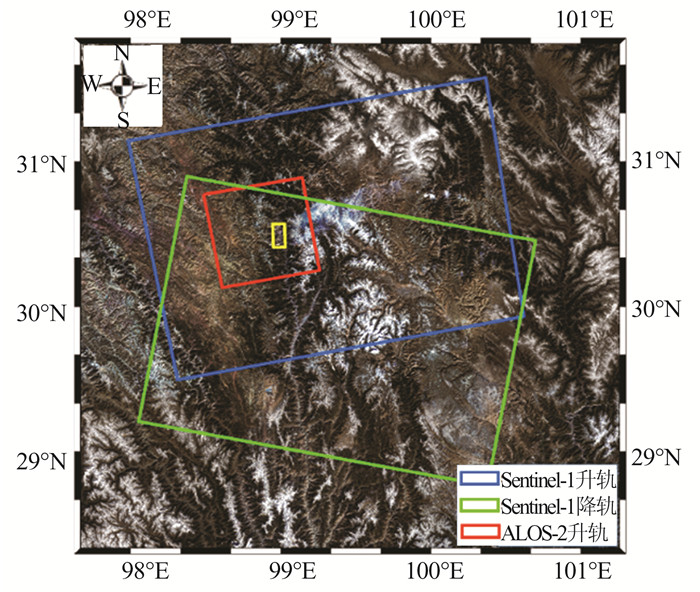
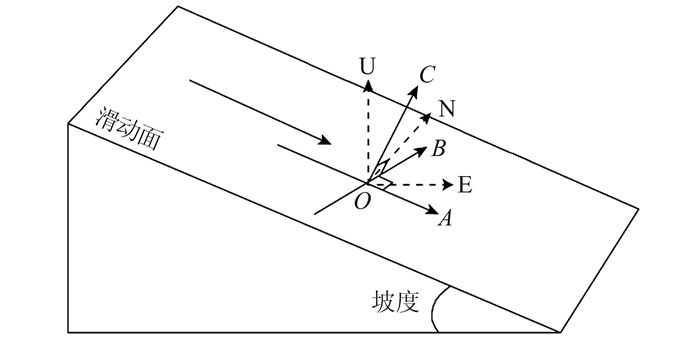
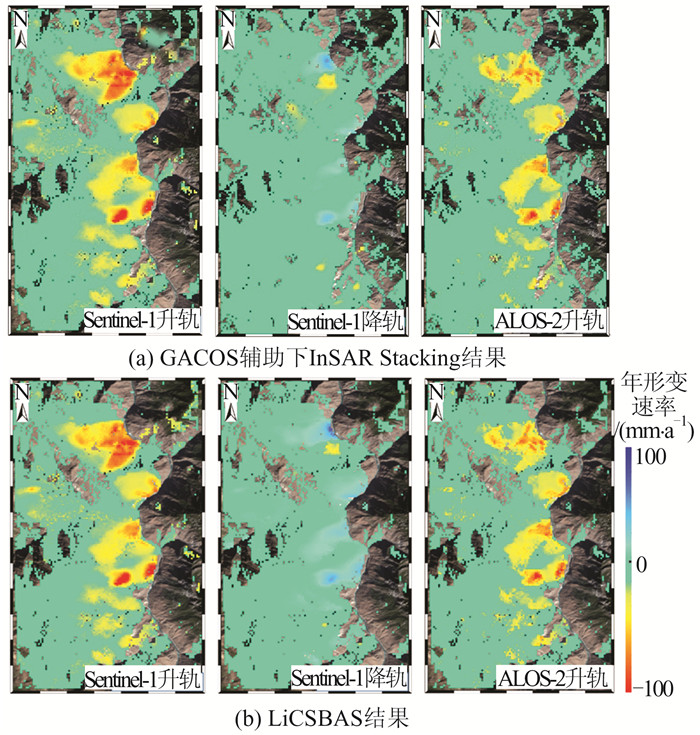
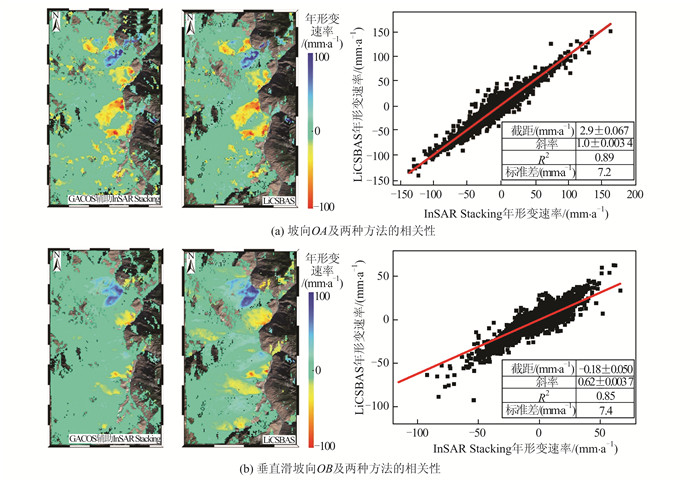
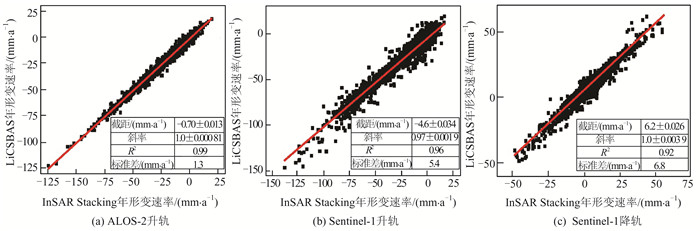
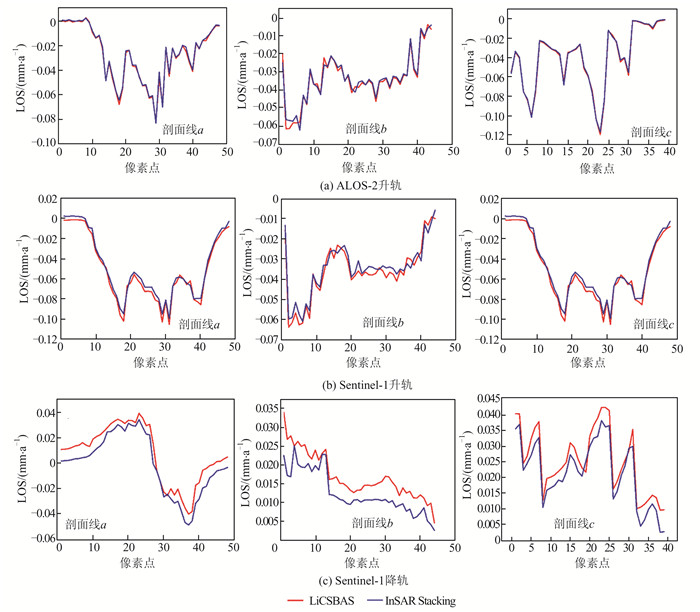
摘要: 西藏自治区贡觉县雄松乡至沙东乡金沙江流域作为川藏铁路的必经河流,地形崎岖、地质灾害隐患点多,亟需对该地区隐患点进行全方位的识别。首先,选取61景哨兵一号(Sentinel-1)升轨影像、53景Sentinel-1降轨影像和7景陆地观测技术卫星2号(advanced land observing satellite 2,ALOS-2)升轨影像对研究区域进行滑坡探测与监测。然后,利用合成孔径雷达(interferometric synthetic aperture radar,InSAR)通用型大气改正在线服务(generic atmospheric correction online service for InSAR,GACOS)辅助干涉影像堆叠技术(InSAR Stacking)的方法,获取研究区域雷达视线(line of sight, LOS)方向的InSAR年形变平均速率图,并结合3个轨道的结果提取出沿坡向和垂直滑坡向的平均速率图。最后,与LiCSBAS时间序列分析包的结果进行比较,发现两者具有高度一致性,LOS向年形变速率图像的相关系数在0.92以上,沿坡向和沿垂直滑坡向年形变速率的相关系数在0.85以上,证明了GACOS辅助下InSAR Stacking结果的可靠性。此外,还发现研究区域内沿坡向最大年形变速率为-163 mm/a;结合InSAR形变结果与光学遥感影像解译,可将该滑坡群分为A~G 7个区域进行实时监测。Abstract:Objectives The Sichuan-Tibet Railway crosses the Jinsha River specifically the section from Xiongsong Town to Shadong Town, Gongjue County, Tibet Autonomous Region, in which exist strong topography variations and many potential geohazards, and hence it urgent to detect the potential geohazards in this region to ensure the railway safety.Methods In this paper, 61 Sentinel-1 ascending, 53 Sentinel-1 descending and 7 advanced land observing satellite 2 (ALOS-2) ascending images are used to derive the annual mean deformation rates in the satellite radar line of sight (LOS) with two advanced InSAR(interferometric synthetic aperture radar) approaches, namely generic atmospheric correction online service for InSAR(GACOS)assisted InSAR Stacking and LiCSBAS. The three LOS annual mean deformation rate maps are then used to determine 2D surface movements (one along the slope and the other perpendicular to the slope) in the study region.Results The comparison between GACOS assisted InSAR Stacking and LiCSBAS results show that they agree with each other with correlation coefficients over 0.92 for the LOS deformation rates and over 0.85 for the 2D deformation rates, suggesting the reliability of GACOS assisted InSAR Stacking. The maximum annual deformation rate of 163 mm/a can be observed in the slope direction and seven landslides (A, B, C, D, E, F, G) can be clearly identified, which in turn lays the foundation for future real-time monitoring. Based on the detailed analysis of the seven regions by using InSAR and optical interpretation results, it is found that the seven landslides had relatively obvious deformation. Landslides A, B, C and D are active landslides, which might cause the result of river blocking due to overall instability. At present, landslides E, F and G are still in the stage of slow deformation.Conclusions This study also find that GACOS assisted InSAR Stacking can effectively remove long-band and topographic related atmospheric delay error with the help of GACOS, which has the advantages of being simple, effective, fast, and easy to popularize and apply. GACOS assisted InSAR Stacking technology can be used to quickly identify potential landslide hazards.
-
Keywords:
- the Jinsha River region /
- landslide detection /
- GACOS /
- InSAR stacking /
- LiCSBAS /
- Sentinel-1 /
- ALOS-2
-
在直线、平面拟合、空间直角坐标变换、自回归模型求解中,系数矩阵和右端观测量由随机和非随机元素组成,且同一随机元素会在不同的位置出现[1-4]。常用的变量含误差(errors-in-variables,EIV)模型及相应的整体最小二乘(total least squares,TLS)方法假设系数阵中所有元素含误差。因此,顾及增广误差矩阵元素的随机特性及其相互关系的结构EIV(structured EIV,SEIV)模型和结构加权整体最小二乘(structured weighted TLS,SWTLS)方法应运而生[5-10]。文献[5]采用极大似然估计方法从含有误差的时间序列数据中确定动态线性系统的参数,被认为是SWTLS问题研究的开端。文献[6]定义了结构整体最小二乘(structured TLS,STLS)这一术语,并将其转换为非线性广义奇异值分解问题求解。文献[7]将结构增广误差矩阵用其中的独立随机元素表示,并命名为约束TLS方法。对于某些列为固定元素而另外一些列为随机元素的混合LS-TLS问题,文献[8]引入正交三角分解计算模型参数。对于误差为非等权相关的情形,文献[9]发展了WLS-WTLS的迭代算法。文献[10]将SEIV模型用部分EIV(partial EIV,PEIV)模型表达,在加权最小二乘准则下推导了参数估计的Gauss-Newton型迭代算法,并进一步给出了参数的一阶近似方差、非线性信赖域区间及偏差。文献[11]给出了PEIV模型的两种迭代算法,其计算效率与系数矩阵中随机元素的数量有关。文献[12]提出了顾及系数阵元素和右端向量相关的广义PEIV模型。文献[13]将系数误差矩阵表示成已知矩阵和独立误差向量的乘积,推导了附有线性和二次约束的STLS问题的迭代算法。文献[14]和文献[15]采用变量投影法将增广系数矩阵表示成仿射结构矩阵与独立随机变量的乘积,然后将STLS问题转换为非线性等式约束优化问题求解。文献[16]研究了含多个右端观测向量的STLS问题。文献[17]提出了结构整体最小范数(structured total least norm,STLN)方法,这一方法可以最小化误差向量的范数,是STLS问题的重要拓展[17-18]。文献[19-20]研究了STLN问题的快速算法。文献[21]将STLN拓展到系数阵和观测向量具有共同元素的情形。针对自回归(auto-regression, AR)模型这一特定STLS问题,文献[3-4]提出了两种新解法。
在STLS算法推导中,不同文献使用了不同的平差准则,其差异在于是否考虑独立误差的重复次数。如二维坐标转换中,源系统的纵横坐标值在系数矩阵中出现了2次,而目标系统的纵横坐标值在右端向量中只出现了1次。文献[1,7,10,13-15]给出的平差准则未考虑重复次数,而文献[3-4,17,21]均考虑了重复次数。不同的平差准则必定会得到不同的平差结果,其参数估值在统计意义上孰优孰劣,目前尚未给出明确结果。本文从函数模型和数值模拟两方面入手,证明了不考虑独立误差元素重复次数的平差准则能够得到统计意义下更优的解。
1 STLS平差模型及平差准则
EIV模型的函数表达式为[1]:
(1a) 式中,
和 分别表示 维观测向量及其误差; 和 分别表示 维系数矩阵及其误差矩阵; 为 维参数向量。误差向量的随机模型为: (1b) 式中,
, 表示矩阵向量化算子,即将 维矩阵的每一列从左至右叠加成一个 维列向量; 是单位权方差; 和 分别是 和 的对称正定协因数矩阵; 表示两者的协因数矩阵。当向量e的协因数矩阵 可逆时,采用WTLS准则求参数的最优估值: (2) 式中,
为 的权矩阵。当系数矩阵具有某种结构时, 为秩亏矩阵无凯利逆。许多学者将EIV函数模型进行改化,一般是从结构误差矩阵或增广误差矩阵中提取独立误差向量,进一步构造目标函数求解。常用的几种EIV模型修正方法如下: 1) PEIV模型及其平差准则。PEIV模型选取系数阵中独立随机量的真值
作为待求量,其函数模型为[10]: (3a) (3b) 式中,
是系数矩阵中随机元素所构成的 维列向量; 和 分别是相应的真值和误差向量; 表示 维单位矩阵; 是已知的 维常数向量,其元素包含系数阵中的非随机元素; 是 维常数矩阵,其形式由系数矩阵中非随机元素的个数及元素间的相关性确定。若 和 相互独立[10],即 ,且两者的方差矩阵为 , ,其中 和 分别为 和 的权矩阵。相应的平差准则为: (4) 可见PEIV的平差准则中没有考虑独立随机误差的重复次数。如果将
和 组合成独立随机误差向量 ,权矩阵 ,则平差准则式(4)可以写为: (5) 因此PEIV模型的SWTLS解是令独立随机误差的加权平方和最小的参数估值。文献[12]中的GPEIV模型、文献[13]中约束结构SWTLS方法和文献[14-15]中的变量投影法,其本质上都是采用式(5)所示的平差准则。
2) STLN模型及其平差准则。STLN方法是定义一个与参数
相关的矩阵 ,提取系数矩阵中的独立随机误差 ,使下式成立[17]: (6) 联立式(1a)和式(6),将观测值残差
表达成系数阵独立误差 和参数 的函数: (7) 将式(7)在
和 的近似值处线性化,舍去二次项后得到线性模型,然后采用下列平差准则[17]: (8) 式中,
, ( )表示 中的第 个元素在误差矩阵 中重复出现的次数。尽管STLN 方法没有考虑误差的权值,但可以很方便地将观测误差的权纳入平差准则。仍令 ,定义 ,由于式(8)中常数项对求极值无影响,则平差准则式(8)等价于: (9) 可见,STLN方法考虑了独立误差
的重复次数,且以重复次数的平方将独立误差纳入平差模型。 3) 虚拟误差模型及其平差准则。文献[3]以AR模型参数估计为背景,将式(1a)所示的EIV模型在观测值的近似值处线性化。设系数阵真值
的近似值为 ,改正数为 ,参数 的近似值为 ,改正数为 ,则线性化方程为: (10) 式中,
表示 对应的改正数。然后通过矩阵等价变换得到 , 和 表示由 按照一定规则构造的近似矩阵; 表示设计矩阵中独立观测值对应的改正数向量。将式(10)化为: (11) 组成虚拟观测值误差方程为:
(12) 联立式(11)和式(12)得到:
(13) 式中,
为所有随机观测值改正数向量; 为等效设计矩阵; 为所有待估参数和虚拟参数的改正数; 表示 的线性变换[3]。采用如下平差准则: (14) 式中,
实际上是 中的独立误差向量 ;Pg=DgP由两部分组成,其中 , ( ,且t+n为独立误差的个数)表示 中的第 个元素在 中的重复次数, 为观测值向量的权矩阵。可见,虚拟误差模型解AR模型这一典型SWTLS问题考虑了重复次数。与STLN方法的差异在于,它采用的是重复次数本身,而不是STLN中重复次数的平方。 上述3种典型的STLS方法采用了不同的平差准则,不同的平差准则一定会得到不同的平差结果。为了比较不同准则下的平差结果,下面将上述3种典型的平差准则下的解纳入到一个统一的平差模型中。
2 STLS模型的通用表达式及算法推导
EIV模型(式(1a))又可以表示为[1]:
(15) 式中,
为 矩阵,其中 为Kronecker积符号,定义为 ,其中 ,且 为任意矩阵。设 为 中的 个独立随机误差向量,则 和 可以分别表示为: (16a) (16b) 式中,
和 分别为 和 矩阵,其元素均为常数。联立式(16a)和式(16b): (17) 将式(17)代入式(15),并令
,则EIV模型可以写为: (18) 独立随机误差的随机模型为:
, (19) 式中,
表示 的协因数矩阵; 表示其权矩阵。令 ,且 出现的次数为 ( )。定义 ,组成综合权矩阵: (20) 相应的平差准则为:
(21) 易知,当
时,式(21)等价于以PEIV模型为代表的准则式(5);当 时,式(21)等价于以STLN模型为代表的准则式(9);当 时,式(21)等价于以虚拟误差模型为代表的准则式(14)。以结构化函数模型(18)为基础,基于平差准则式(21),构造如下Lagrange目标函数: (22) 式中,
为 维Lagrange乘子向量。令目标函数式(22)对各待定量 的偏导数为0,可得: (23a) (23b) (23c) 由式(23b)得到独立误差向量
的估值为: (24) 式中,
,表示综合权矩阵的逆; 分别为 的估值。将式(24)代入式(23c)并移项可得: (25) 将式(25)代入式(23a)可以得到法方程:
(26) 则参数的估值为:
(27) 由于式(26)法方程矩阵不对称,若在式(26)两端加上
,那么 可由下式估计: (28) 根据上述推导过程,可以得出通用模型计算SWTLS问题的迭代步骤为:
1) 给定
、 、 ,根据 的重复次数和不同平差准则的计入方式确定对角阵 ,根据 的结构确定 和 。采用式(20)计算综合权阵 和对应的协因数矩阵 。计算 和参数的初值 ; 2) 根据初值
计算矩阵 和 。采用式(25)和式(24)分别计算 和 ,然后由式(16a)计算 的值,从而有 , 是 的逆运算,表示将 向量恢复成 维矩阵; 3) 将
、 、 、 分别代入式(27)或式(28),计算参数估值 ; 4) 如果最后两次的估值
足够接近于给定的阈值,终止迭代。否则,转向步骤2)。 3 STLS模型平差准则的优化选取
尽管由式(18)和式(19)组成的SWTLS一般模型能通过选取不同的
矩阵获得不同准则下的迭代最优解,但无法获得参数的方差或均方误差(mean square error,MSE)等精度评定指标,只能在模拟实验中检验参数精度。由文献[22-23]可知,WTLS并不是一种新的平差方法,仅仅是LS框架下的另外一种平差模型,且经典平差理论中的Gauss-Helmert(GH)模型(附有参数的条件平差模型)是EIV模型的一个特例。因此WTLS问题的解可由非线性GH模型导出。若给定 的近似值 和 的近似值 ,式(18)可线性化为: (29) 式中,
; ; 和 为近似值 和 处的 和 的值。且有: (30) (31) 将式(30)和式(31)代入式(29)并作适当变换可以得到:
(32) 可见SEIV模型的线性化形式(式(32))是一个标准GH模型,该模型不再体现
的重复次数,实际上重复次数已经由投影矩阵 表达了。重复次数体现了EIV模型的结构性,而投影矩阵 正是描述上述结构性的量。根据经典LS理论,其平差准则应为: (33) 因此,从SWTLS问题的线性化形式证明了其平差准则应满足式(33)。由线性化模型式(32)得到的最小二乘解是在给定
和 情形下的一个近似解,为了得到更严密的解,将式(32)进一步表达为: (34) 式中,
。为了与§2中符号一致,记 ( 为t维单位矩阵)。根据式(34)及平差准则式(33),构造如下Lagrange乘子函数: (35) 分别求
对 、 和 的偏导数,并令其值为0,可得: (36) (37) (38) 由式(37)可得:
(39) 将式(39)代入式(38)得:
(40) 由式(40)可得Lagrange乘子向量为:
(41) 式(40)两边同乘以
并顾及式(36),则有: (42) (43) 由GH模型推导得到的参数估计(式(43))与§2中通用模型得到的解(式(28))具有完全相同的形式。GH模型的算法流程如下:
1) 给定
、 、 ,根据 的结构确定 、 。计算 和参数的初值 ,使用上标(i) 对不同迭代次数下的各参数进行区分,则 和 的初值分别为 和 ; 2) 将
代入式(31)计算 和 ,由式(41)计算 ,由式(39)计算 并更新 ,由式(30)计算 ; 3) 由式(42)计算
; 4) 如果
小于给定的阈值,则终止迭代;否则,更新 ,转向步骤2)。 注意,若不限定式(35)中
,那么采用线性化的GH模型,在准则式(21)下,即可选取不同类型 矩阵的条件下,可以得到和§2中通用模型完全一致的解。采用GH模型进行算法推导有3个方面的意义:(1)证明了SEIV模型的平差准则中不应该再考虑重复矩阵。(2)证明了由通用模型(式(18))和线性化GH模型作为条件,在相同的平差准则下得到的参数估值是一致的。(3)将SEIV模型线性化后,便于采用协方差传播定律计算参数估值的近似精度。 4 STLS模型参数估值的近似方差
根据§2、§3的算法得到SWTLS解以后,可计算独立误差向量的估值
,单位权方差计算式为: (44) SWTLS解的近似协因数矩阵可以根据线性化GH模型的解(式(42))求解。虚拟观测值
可以写成: (45) 式中,
为 中的 个独立随机观测向量。根据协因数传播律,向量 的协因数矩阵为: (46) 实际计算中近似值
可以用SWTLS估值 代替,相应的残差矩阵近似值 用对应的估值 代替。如果忽略式(42)中 这一项中 的随机性,那么可由协因数传播律得到SWTLS解的近似协因数矩阵为: (47) 从而得到SWTLS解的近似方差为:
(48) 5 数值实验
首先采用二维仿射变换实例验证算法的正确性和可行性。设第
个公共点 在源坐标系和目标坐标系中的坐标分别为 和 ,仿射变换模型为 , ,其中 和 为两个坐标系的平移量, 、 、 、 分别表示两个坐标系之间的旋转和尺度变换参数。假设有3个或以上的公共点,仿射变换模型可以用EIV模型(式(1))表示,且有: , (49) 给定12个公共点在源坐标系中的坐标分别为(-1,1)、(1.2,-3.0)、(-2.6,3.0)、(3.0,1.5)、(-4.8,-1.0)、(5.2,0.2)、(6.0,5.5)、(-7.2,2.2)、(7.8,-2.0)、(8.5,2.2)、(-9.5,-5.0)、(10.0,-0.8),参数的真值为
=[10 4 -2 -10 1 3]T,根据仿射变换模型计算出12个点在目标系中的真实坐标分别为(4,-8)、(20.8,-17.8)、(-6.4,-3.6)、(19.0,-2.5)、(-7.2,-17.8)、(30.4,-4.2)、(23.0,12.5)、(-23.2,-10.6)、(45.2,-8.2)、(39.6,5.1)、(-18.0,-34.5)、(51.6,-2.4)。对所有坐标值添加方差为 ( 为 的单位矩阵)的随机误差。首先,不考虑系数矩阵中源坐标重复2次而目标坐标重复1次的差异,取重复矩阵 时,分别采用本文方法、PEIV模型[10]和变量投影法[14]进行求解,得到的参数估计结果如表1所示。 当取
(4和1的个数都为24)时,采用本文方法和STLN方法[17]进行求解,得到的参数估计结果如表2所示。 表 2 不同平差方法的SWTLS解() Table 2. SWTLS Solutions with Different Adjustment Methods () 平差方法 STLN方法[17] 10.418 681 4.056 913 -2.101 082 -9.639 440 1.118 336 2.855 364 本文方法 10.418 681 4.056 913 -2.101 082 -9.639 440 1.118 336 2.855 364 从表1可以看出,由于PEIV模型[10]、变量投影法[14]均未考虑源系统中坐标的重复次数,两者的平差准则等价于本文提出的通用模型中重复矩阵取单位矩阵时的准则(式(21)),尽管三者对结构误差的处理采用了不同的函数模型,但在相同的准则下都得到了完全一致的平差结果,说明本文提出的通用平差算法是可行有效的。由表2可以看出,STLN方法[17]顾及了系数阵中随机观测值的重复次数,并且是将观测重复数的平方纳入平差模型,和本文通用模型在同样的平差准则下也得到了一致的平差结果,进一步证明了本文算法的可行性和有效性。
为了验证不同平差准则下SWTLS解的统计性质,模拟系数阵元素和右端项含有公共元素的SEIV模型,系数阵和右端项的真值及误差的结构分别为:
(50) (51) 待估参数的真值为
,独立误差向量 是零均值独立同分布的随机变量,其方差为 ,其中 表示25×25阶单位矩阵, ( )的重复次数 由 的结构获得。分别采用3种平差准则计算参数的估值,准则式(21)中对应的 矩阵分别取 , ,D3=diag( , , , )=diag(1,9,1,9, ,1,9,1)。根据式(44)和式(48)计算单位权方差和参数估值的方差。由于参数真值已知,可以计算均方误差 ,以此来检核3种平差准则下估值的精度,并与近似方差对照。分别取误差水平 和 进行计算。为了体现结果的统计性,将不同误差水平的实验各进行10 000次,将每次运算的结果取平均值,结果分别见表3和表4。 表 3 不同平差准则下的SWTLS结果() Table 3. SWTLS Results Under Different Adjustment Principles () 统计项 统计量 估计参数值 0.999 998 1.000 281 0.999 975 5.002 389 5.007 359 5.009 953 1.999 596 1.999 320 1.998 190 单位权方差 0.239 737 0.537 349 1.463 591 参数方差估值 9.43×10-6 1.72×10-5 5.76×10-5 5.23×10-4 9.14×10-4 3.19×10-3 8.28×10-6 1.60×10-5 5.05×10-5 5.40×10-4 9.47×10-4 3.30×10-3 MSE 9.76×10-6 1.10×10-5 1.63×10-5 5.44×10-4 6.21×10-4 9.40×10-4 8.50×10-6 9.39×10-6 1.42×10-5 5.63×10-4 6.41×10-4 9.71×10-4 表 4 不同平差准则下的SWTLS结果() Table 4. SWTLS Results Under Different Adjustment Principles () 统计项 统计量 估计参数值 1.000 220 1.003 770 1.007 659 4.997 838 5.022 963 5.049 989 2.000 725 2.004 000 2.007 714 单位权方差 0.960 341 2.146 473 5.839 121 参数方差估值 3.78×10-5 6.87×10-5 2.30×10-4 2.09×10-3 3.65×10-3 1.27×10-2 3.32×10-5 6.41×10-5 2.02×10-4 2.17×10-3 3.78×10-3 1.32×10-2 MSE 4.02×10-5 4.50×10-5 6.67×10-5 2.21×10-3 2.53×10-3 3.85×10-3 3.53×10-5 3.88×10-5 5.82×10-5 2.29×10-3 2.62×10-3 3.97×10-3 从表3可以看出,不考虑重复次数的平差准则(采用
)获得的参数估值更接近于真值。参数各分量的MSE最小,从数值上验证了不考虑系数阵误差重复系数的平差准则是最优的。单位权方差的估值略小于真值,是由于式(43)没有考虑非线性模型线性化引入的偏差项。同理,各参数分量的方差均小于对应的MSE,原因是SEIV模型的非线性特性会引入估计偏差,方差加上偏差的平方和等于MSE。但是,对比方差和MSE的差异可知,参数3个分量的方差估值和MSE之间的差异( )分别为3.38%、3.86%和2.59%,说明当误差较小时,参数方差估值和MSE的差异很小,可以作为精度评定的指标。因此,本文不再采用非线性最小二乘偏差修正或Monte Carlo模拟的思想求解偏差值[10,24]。 从上述理论分析可知,将SEIV模型线性化后,其平差准则不应顾及误差重复次数。式(44)和式(48)只适用于
为单位阵的情形。从后面两列可以看出,当平差准则中计入误差重复的次数时,单位权方差估值与真值以及参数分量的方差估值与MSE均有较大的差异。当 时,单位权方差估值约为真值的6倍,方差估值约为对应MSE的3.5倍,这是由于单位权方差公式中重复计算残差平方和所致,由此进一步证明不能采用这两种平差准则用线性近似方法求单位权中误差及方差。 由表4可知,增大观测误差的方差,能够得到与表3一致的结论,进一步验证了最优平差准则应该选择重复矩阵
为单位阵。由式(48)给出的方差估值与MSE在3个分量上的偏差分别为5.97%、5.43%、5.95%,进一步证明了本文的近似精度评定方法在误差较小的情况下是可行有效的。 6 结语
结构EIV模型系数矩阵中的随机元素重复出现的次数是否应计入平差准则以及如何计入平差准则,目前尚未形成定论。本文从模型分析和数值验证两方面入手,证明重复次数不应计入平差准则。主要贡献如下:
1)总结了已有的3种处理SEIV模型的平差准则,指出不同的平差准则会得到不同的平差结果。提出了一种通用的SWTLS平差模型,通过选取不同的综合权矩阵
得到的目标函数等价于上述3种不同准则下的目标函数。采用Lagrange乘子法推导了通用模型的解并给出了计算步骤。 2)迭代方法无法给出参数的统计性质,本文将通用模型线性化得到GH模型,从理论上分析了误差重复次数不应计入平差准则的原因。推导了GH模型的算法,证明其与通用模型得到的结果是一致的。根据误差传播律得到了参数的近似方差估值。
3)通过实例验证了本文提出的算法与已有方法结果一致,证明了本文方法可行有效。通过模拟计算证明了不考虑误差重复次数的平差准则得到的解在MSE意义下最优,且参数的近似方差是MSE的良好近似,可以作为精度评定的指标。
-
表 1 ALOS-2升轨影像干涉对
Table 1 ALOS-2 Ascending Interferograms
序号 主影像 从影像 垂直基线/m 时间基线/d 1 20170724 2017112 50 126 2 20170724 2018052 -226 308 3 20170724 2018072 -128 364 4 20170724 2018111 50 476 5 20170724 2019052 -109 672 6 20170724 2019072 -102 728 7 20171127 2018052 -277 182 8 20171127 2018072 -178 238 9 20171127 2018111 1 350 10 20171127 2019052 -159 546 11 20171127 2019072 -153 602 12 20180528 2018072 98 56 13 20180528 2018111 277 168 14 20180528 2019052 117 364 15 20180528 2019072 124 420 16 20180723 2018111 178 112 17 20180723 2019052 19 308 18 20180723 2019072 25 364 19 20181112 2019052 -159 196 20 20181112 2019072 -153 252 21 20190527 2019072 6 56 -
[1] 许强, 李为乐, 董秀军, 等. 四川茂县叠溪镇新磨村滑坡特征与成因机制初步研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(11): 2 612-2 628 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201711002.htm Xu Qiang, Li Weile, Dong Xiujun, et al. The Xinmo Village Landslide on June 24, 2017 in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province: Characteristics and Failure Mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(11): 2 612-2 628 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201711002.htm
[2] Ouyang C J, Zhao W, Xu Q, et al. Failure Mechanisms and Characteristics of the 2016 Catastrophic Rockslide at Su Village, Lishui, China[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(7): 191-100 http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dalei_Peng/publication/324588780_Failure_mechanisms_and_characteristics_of_the_2016_catastrophic_rockslide_at_Su_village_Lishui_China/links/5adff9afa6fdcc29358fe239/Failure-mechanisms-and-characteristics-of-the-2016-catastrophic-rockslide-at-Su-village-Lishui-China.pdf
[3] 许强, 郑光, 李为乐, 等. 2018年10月和11月金沙江白格两次滑坡-堰塞堵江事件分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(6): 1 534- 1 551 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201806016.htm Xu Qiang, Zheng Guang, Li Weile, et al. Study on Successive Landslide Damming Events of Jinsha River in Baige Village on Octorber 11 and November 3, 2018 [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26 (6): 1 534-1 551 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201806016.htm
[4] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 957-966 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190088 Xu Qiang, Dong Xiujun, Li Weile. Early Identification, Monitoring and Early Warning of Major Geolhazards Based on Space-Air-Ground[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190088
[5] 许强. 对地质灾害隐患早期识别相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2020, 45(11): 1 651-1 659 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200043 Xu Qiang. Understanding and Consideration of Related Issues in Early Identification of Potential Geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1 651-1 659 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200043
[6] Dai Keren, Li Zhenhong, Xu Qiang, et al. Entering the Era of Earth Observation-Based Landslide Warning Systems: A Novel and Exciting Framework[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(1): 136-153 doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2954395
[7] Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8-20 doi: 10.1109/36.898661
[8] Canuti P, Casagli N, Ermini L, et al. Landslide Activity as a Geoindicator in Italy: Significance and New Perspectives from Remote Sensing[J]. Environmental Geology, 2004, 45(7): 907-919 doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0952-5
[9] Metternicht G, Hurni L, Gogu R. Remote Sensing of Landslides: An Analysis of the Potential Contribution to Geo-Spatial Systems for Hazard Assessment in Mountainous Environments[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 98(2): 284-303 http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20053194375.html
[10] Van Westen C J, Castellanos E, Kuriakose S L. Spatial Data for Landslide Susceptibility, Hazard, and Vulnerability Assessment: An Overview[J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 102(3): 112-131 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0013795208001786
[11] Casagli N, Catani F, Del Ventisette C, et al. Monitoring, Prediction, and Early Warning Using Ground-Based Radar Interferometry[J]. Landslides, 2010, 7(3): 291-301 doi: 10.1007/s10346-010-0215-y
[12] Martha T R, Kerle N, Jetten V, et al. Characterising Spectral, Spatial and Morphometric Properties of Landslides for Semi-Automatic Detection Using Object-Oriented Methods[J]. Geomorphology, 2010, 116(1): 24-36 http://www.researchgate.net/profile/CJ_Westen/publication/222579232_Characterising_spectral_spatial_and_morphometric_properties_of_landslides_for_semi-automatic_detection_using_object-oriented_methods/links/02bfe50d1e7b641a49000000
[13] Guzzetti F, Mondini A C, Cardinali M, et al. Landslide Inventory Maps: New Tools for an Old Problem[J]. Earth - Science Reviews, 2012, 112(1): 42-66 http://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/82520789.pdf
[14] Ye X, Kaufmann H, Guo X F. Landslide Monitoring in the Three Gorges Area Using D-InSAR and Corner Reflectors[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2004, 70(10): 1 167-1 172 http://essential.metapress.com/content/k3v513t523111536/fulltext.pdf?page=1
[15] 李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用: 挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 967-979 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190098 Li Zhenhong, Song Chuang, Yu Chen, et al. Application of Satellite Radar Remote Sensing in Landslide Detection and Monitoring: Challenges and Solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 967-979 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190098
[16] Tofani V, Segoni S, Agostini A, et al. Technical Note: Use of Remote Sensing for Landslide Studies in Europe[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2013, 13(2): 299-309 doi: 10.5194/nhess-13-299-2013
[17] Riddick S N, Schmidt D A, Deligne N I. An Analysis of Terrain Properties and the Location of Surface Scatterers from Persistent Scatterer Interferometry[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2012, 73: 50-57 doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.05.010
[18] LiZ H, Fielding E J, Cross P, et al. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Atmospheric Correction: GPS Topography-Dependent Turbulence Mode l[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2006, 111(B2): B02404 doi: 10.1029/2005JB003711/pdf
[19] Gong W, Meyer F J, Liu S Z, et al. Temporal Filtering of InSAR Data Using Statistical Parameters from NWP Models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(7): 4 033- 4 044 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2389143
[20] Torres R, Snoeij P, Geudtner D, et al. GMES Sentinel-1 Mission[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 120: 9-24 doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.05.028
[21] Werner C, Wegmüller U, Strozzi T, et al. Gamma SAR and Interferometric Processing Software[C]. The 2000 ERS - Envisat Symposium, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2000
[22] Yagüe-Martínez N, Prats-Iraola P, Rodríguez González F, et al. Interferometric Processing of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 2 220- 2 234 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2497902
[23] Yu C, Penna N T, Li Z H. Generation of RealTime Mode High-Resolution Water Vapor Fields from GPS Observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017, 122(3): 2 008-2 025 doi: 10.1002/2016JD025753
[24] Wright T, Parsons B, Fielding E. Measurement of Interseismic Strain Accumulation across the North Anatolian Fault by Satellite Radar Interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(10): 2 117-2 120 doi: 10.1029/2000GL012850
[25] Xiao R Y, Yu C, Li Z H, et al. General Survey of Large-Scale Land Subsidence by GACOS-Corrected InSAR Stacking: Case Study in North China Plain[J]. Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences, 2020, 382: 213-218 doi: 10.5194/piahs-382-213-2020
[26] Morishita Y, Lazecky M, Wright T, et al. LiCSBAS: An Open-Source InSAR Time Series Analysis Package Integrated with the LiCSAR Automated Sentinel-1 InSAR Processor[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3): 424 doi: 10.3390/rs12030424
[27] 李永生, 张景发, 李振洪, 等. 时序InSAR离散相干点相位解缠误差检查与校正方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报· 信息科学版, 2014, 39(10): 1 199-1 203 http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/3095 Li Yongsheng, Zhang Jingfa, Li Zhenhong, et al. Detection and Correction of Phase Unwrapping Errors in InSAR Time Series Analysis with Discrete Coherent Points[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(10): 1 199-1 203 http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/3095
[28] Hu X, Lu Z, Pierson T C, et al. Combining InSAR and GPS to Determine Transient Movement and Thickness of a Seasonally Active Low-Gradient Translational Landslide[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(3): 1 453-1 462 doi: 10.1002/2017GL076623





 下载:
下载: