Improved Gravity-Geologic Method and Its Application to Seafloor Topography Inversion in the South China Sea
-
摘要: 为进一步提高传统重力地质法(gravity-geologic method,GGM)反演海底地形的精度,顾及海底地形非线性项对GGM进行改进。采用改进的GGM反演了中国南海地区空间分辨率为1'×1'海底地形模型,并利用船测水深检核点对反演结果进行了精度评定,验证了所提方法的有效性。研究结果表明,忽略海底地形非线性项会在起伏约2 km的山区引起约50 mGal偏差;改进的GGM能有效地从短波重力异常中恢复海底地形的非线性项;获取的海底地形结果与ETOPO1、SIOV23.1及传统GGM反演模型相比具有最高的精度,与检核点差异的均方根为130.4 m;与传统GGM法反演结果相比,改进GGM获得的结果在黄岩海山链附近精度提高10.8 m,在中沙群岛附近精度提高4.7 m。Abstract:Objectives The accuracy of the traditional gravity-geologic method (GGM) for inversion of seafloor topography should be improved.Methods This paper proposes an improved GGM (iGGM) consi-dering the nonlinear term.The 1 arc minute seafloor topography of the South China Sea is inverted by iGGM, and its accuracy is evaluated through check points to verify the effectiveness.Results The results show that neglecting nonlinear term of seafloor topography results in a deviation of approximately 50 mGal in mountainous areas with undulation of approximately 2 km. The nonlinear term of seafloor topography could be recovered by the iGGM from short-wavelength gravity anomaly.Conclusions Compared with the traditional GGM, ETPO1 and SIO V23.1, iGGM has the best accuracy. The root mean square of deviations between iGGM and check points is 130.4 m. Compared with traditional GGM, the improvement of iGGM is 10.8 m near the Huangyan seamount chain, and it is 4.7 m near the Zhongsha Islands.
-
Keywords:
- seafloor topography /
- gravity anomaly /
- gravity-geologic method /
- nonlinear term
-
海洋面积占全球总面积约71%,确定精细的海底地形图对海洋资源开采、水下导航、海底构造运动和海洋环流等研究具有重要意义。船载声呐探测技术是目前获取深海海底地形的主要手段。然而,该方法成本高、耗时长。有学者估计,要完成全球深海的船载测深工作大约需要200年,且耗资数十亿美元[1]。随着卫星测高技术的发展,通过其海面高数据反演的海洋重力场已具有较高的分辨率和精度,且能实现全球海域的均匀覆盖。当前,卫星测高海面重力异常的解算精度已达2~3 mGal[2]。海底洋壳与海水层间存在密度差,海底地形变化势必引起海洋重力场的扰动。因此,若能构建出海面重力异常和海底地形间的数学关系,就能实现海底地形的反演。目前已有许多海底地形反演方法被提出,主要包括线性回归法[3]、导纳函数法[4]、最小二乘配置法[5]、重力地质法(gravity-geologic method,GGM)[6-12]和模拟退火法[13]等。其中,GGM简单高效,能够满足大范围水深反演的需要[12]。
GGM起初可以通过观测重力异常和少量钻孔资料预测沉积基底深度[14]。由于沉积层密度的垂向变化较大,其效果欠佳。受益于海底洋壳与海水层的密度差几乎不随深度变化,GGM被广泛用于海底地形反演[6-7, 15]。GGM通过船测水深控制点从观测重力异常中分离长波重力异常和短波重力异常,并利用短波重力异常反演海底地形。许多学者对GGM中密度差的确定和长波重力异常的构建进行了相关研究。文献[7]采用迭代法确定密度差的经验值;文献[8]提出确定密度差的向下延拓法;文献[9]采用改进的重力地质方法(improved gravity-geologic method,iGGM)来逼近长波重力异常,有效改善了由不均匀控制点构建长波重力异常的精度;文献[16]将iGGM法应用于几内亚湾海底地形绘制,取得了较好效果,并指出对于山区反演,应采用更多的船测点及不同的最佳密度差;文献[10]考虑地形因素的影响,提出了一种基于普通克里金的地形约束因子权重优化方法来构建区域重力异常。
短波重力异常是除密度差和长波重力异常外影响GGM反演质量的另一重要因素。传统GGM使用布格板公式计算由海底地形起伏引起的短波重力异常,这是一种线性近似处理,势必会造成信息的遗漏[4]。文献[17]提出在计算短波重力异常时顾及局部地形改正,大大提高了海底地形的反演精度;文献[11]在构造短波重力异常时,采用三维直角棱柱代替布格板公式,并在西菲律宾盆地验证其方法的有效性。上述研究采用空间域积分解算地形重力效应,计算效率低,在一定程度上与GGM计算速度快且适用于大范围海域等优点相悖。此外,传统GGM利用短波重力异常恢复海底地形时,同样基于布格板公式解算,仅能恢复海底地形的线性信息。
基于上述问题,本文提出了一种改进的GGM,利用频率域重力正演和迭代反演方法恢复海底地形的非线性项,选择中国南海作为研究区,构建空间分辨率为1'×1'海底地形模型,并详细分析了影响模型精度的各种因素。
1 原理与方法
1.1 传统GGM原理
海面观测重力异常可看作两部分之和,由海底地形起伏引起的短波重力异常和由深部密度不均引起的长波重力异常,其表达式为:
$$ {g}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{s}}\left(i\right)={g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(i\right)+{g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(i\right) $$ (1) 式中,$ i $表示对应于观测重力异常格网点的位置;$ {g}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{s}} $、$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}} $和$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}} $分别表示观测重力异常、短波重力异常和长波重力异常。
已知水深控制点处的$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $可以通过布格板公式近似计算,计算式为:
$$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right)=2\mathrm{\pi }G\Delta \rho \left(E\left(j\right)-D\right) $$ (2) 式中,$ G $是万有引力常量;$ j $表示已知水深控制点的位置;$ E\left(j\right) $为已知控制点水深;$ D $为参考深度,通常取测深点的最大深度;$ \Delta \rho $为海底洋壳与海水间的密度差。由式(1)和式(2)可得:
$$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(j\right)={g}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{s}}\left(j\right)-{g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $$ (3) 式中,$ {g}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{s}}\left(j\right) $为控制点处的观测重力异常,可由实际观测重力异常数据插值得到;$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(j\right) $为控制点处的长波重力异常,经格网化处理后可获得任意格网点上的长波重力异常$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(i\right) $;根据式(1)可计算出格网点上的$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(i\right) $,应用布格板公式将$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(i\right) $转换为海底地形起伏,再添加参考深度,可获得水深格网模型$ E\left(i\right) $:
$$ E\left(i\right)=\frac{{g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(i\right)}{2\mathrm{\pi }G\Delta \rho }+D $$ (4) 在GGM计算过程中,共涉及$ \Delta \rho $和$ D $两个参数。其中,反演结果几乎不受$ D $取值的影响,但对$ \Delta \rho $的变化十分敏感。$ \Delta \rho $的理论值为1.67 g/cm3,等于海底基岩密度2.70 g/cm3与海水密度1.03 g/cm3之差[6]。大量实践表明,GGM中$ \Delta \rho $通常远偏离于理论值,因而不具备实际物理意义,仅为经验参数[7-8, 12]。常用的$ \Delta \rho $确定方法主要有向下延拓法和迭代法[7-8]。本文采用迭代法,按一定的步长改变$ \Delta \rho $,并反演对应的水深模型。通过计算反演模型与船测水深值间的相关系数及标准差(standard deviation,STD),选取最小STD及最大相关系数对应的$ \Delta \rho $为最优密度差。
1.2 短波重力异常计算
观测重力异常的精度、水深控制点分布、所采用的插值/格网化方法、海底地形起伏状况等因素均会影响GGM的模型构建精度。传统GGM通常在平坦地形区具有较高的精度,而在复杂地形区精度较低。该现象一定程度上归咎于传统GGM仅考虑海底地形的线性项,而忽略非线性项。在式(2)中,若设定$ D=0 $,则$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $与海底地形间通过布格板项$ 2\mathrm{\pi }G\Delta \rho E\left(j\right) $表示为一一对应的线性关系,而实际上海面重力异常与海底地形间应为非线性关系[11]。文献[17]将$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $表示为局部地形改正项$ \mathtt{δ}{g}_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{C}} $和布格板项之和,计算式为:
$$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right)=2\mathrm{\pi }G\Delta \rho E\left(j\right)+\mathtt{δ}{g}_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{C}} $$ (5) 传统GGM仅考虑式(5)中的线性部分,而忽略非线性项$ \mathtt{δ}{g}_{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{C}} $。这在平坦地形区是可行的,然而在复杂地形区,忽略非线性项会引入系统误差,从而降低反演精度[17]。$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $除了按式(5)表示外,亦可直接表示为:
$$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right)=\Delta g\left(x, y, z, E, \Delta \rho \right) $$ (6) 式中,$ (x, y, z) $为计算点三维坐标;$ E $为海底深度。
为了兼顾精度与计算效率,本文采用文献[18]的Parker公式计算短波重力异常,公式为:
$$ F\left(\Delta g\right(i\left)\right)=2\mathrm{\pi }G\Delta \rho {\mathrm{e}}^{-\left|\overrightarrow{k}\right|d}\sum\limits_{n=1}^{{\infty }}\frac{{\left|\overrightarrow{k}\right|}^{n-1}}{n!}F\left({E}^{n}\right(i\left)\right) $$ (7) 式中,$ F $表示二维傅里叶变换;$ \overrightarrow{k} $为圆波数;$ \Delta g\left(i\right) $为海底地形产生的重力异常;$ d $是海底地形的平均深度;$ n $是级数展开阶数。
该方法可借助快速傅里叶变换(fast Fourier transform,FFT)技术在频率域中解算,因而十分高效。式(7)仅能计算与$ i $位置对应的格网点重力值,无法直接计算离散控制点$ j $处的重力值。为此,本文按1'的格网分辨率计算落入同一格网单元内控制点的平均值,以此作为新的控制点。新控制点位置$ j\in i $,从而可从$ \Delta g\left(i\right) $中直接提取$ \Delta g\left(j\right) $,即为控制点上的$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $。
1.3 海底地形反演
传统GGM利用式(5)反演海底地形时,同样未顾及非线性项,仅利用布格板公式将短波重力异常转换为水深值。尽管经由一系列处理得到的短波重力异常与海底地形间存在强线性关系,但其非线性部分仍具有一定贡献[4, 13, 19]。本文采用一种迭代技术来恢复海底地形的非线性项,计算式为:
$$ {E}^{k}={E}^{k-1}+\frac{\Delta {g}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}}\left({E}^{k-1}\right)}{2\mathrm{\pi }G\Delta \rho } $$ (8) $$ \Delta {g}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}}\left({E}^{k-1}\right)={g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}-{g}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}}\left({E}^{k-1}\right) $$ (9) 式中,$ k=\mathrm{1, 2}, \dots , N $为迭代次数;$ {E}^{k} $为第$ k $次迭代解算的海底地形模型,$ {E}^{0} $由式(4)计算获得;$ \Delta {g}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}} $表示残余重力异常;$ {g}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} $表示海底地形模型正演重力异常,由式(7)计算。
上述方法利用迭代线性缩放来估计非线性项,计算简单,无需大规模矩阵运算。迭代停止条件可设定为$ \Delta {g}_{\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{s}} $的均方根(root mean square,RMS)小于海面重力异常观测精度或进行了若干次迭代。决定式(8)能否准确收敛的关键是重力正演计算的精度[20]。
综上所述,本文所提的改进GGM计算步骤如下:
1)将离散的船测水深控制点按1'格网分辨率,通过块平均值操作生成新的控制点。
2)新控制点格网化或采用现有模型填充,生成初始海底地形模型。
3)利用式(7)和初始模型正演控制点处的短波重力异常$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(j\right) $。
4)将观测重力异常插值到控制点上获得$ {g}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{b}\mathrm{s}}\left(j\right) $,并根据式(3)计算控制点上的长波重力异常$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(j\right) $。
5)控制点$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(j\right) $格网化生成长波重力异常格网$ {g}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}\left(i\right) $,并从观测重力异常中扣除,从而获得短波重力异常格网$ {g}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{t}}\left(i\right) $。
6)利用式(8)迭代估计海底地形模型$ {E}^{k}\left(i\right) $。
2 数值实验与分析
2.1 实验数据
本文选择中国南海112°E~119°E、12°N~20°N范围为研究区,为避免频率域计算的边缘效应,研究区沿四周外扩5'。实验使用的数据包括:
1)海底地形模型。SRTM15+V2.4为美国斯克里普斯海洋研究所(Scripps Institution of Oceanography,SIO)发布的15″分辨率全球水深地形模型,在本文中用于船测水深数据的粗差剔除[21]。SIO V23.1为SIO发布的全球海底地形模型,空间分辨率1'[3]。ETOPO1为美国国家地球物理数据中心(National Geophysical Data Center,NGDC)在2008年发布的1'全球地形模型[22]。上述模型已被广泛使用,其精度反映了当前海底地形反演技术水平,在本文中用于验证反演方法的有效性。
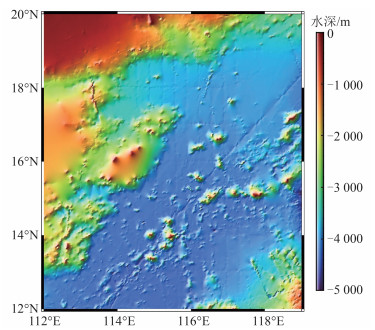
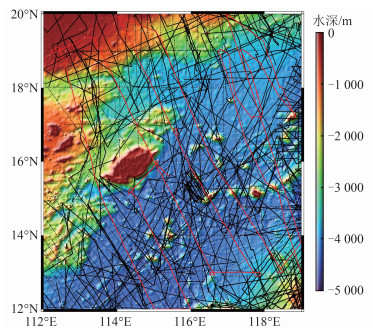
2)船测水深数据。由NGDC提供研究区内合计136 028个测深点。由于船测水深数据时间跨度大,观测质量参差不齐,因而存在较多粗差数据。本文以SRTM15+V2.4模型为基础,将模型水深插值到船测点上,并剔除两者差异大于两倍中误差的数据点。共剔除粗差点4 531个,保留数据点131 497个,数据剔除率3.33%。考虑到同一测线上船测水深的相关性,若按随机或每隔3个控制点选一个检核点的方法,可能导致插值模型的检核精度虚高。本文以SO49和V3604两条航迹线上的测深点作为检核点,其余数据作为控制点。研究区船测点分布见图 1,其中黑色线为控制点,共105 512个,红色线为检核点,共25 985个,检核点与控制点数量比例约为1∶4,背景水深为SRTM15+V2.4模型。
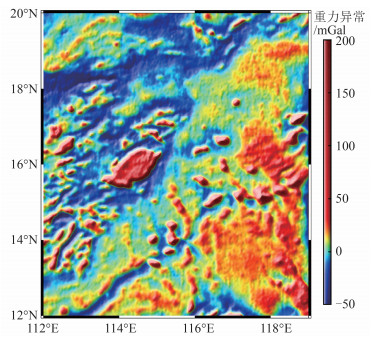
3)测高重力异常数据。采用SIO最新发布的1'空间分辨率海面重力异常模型grav_31.1,如图 2所示。
2.2 密度差确定
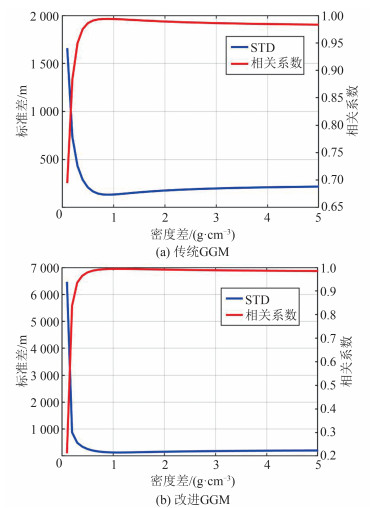
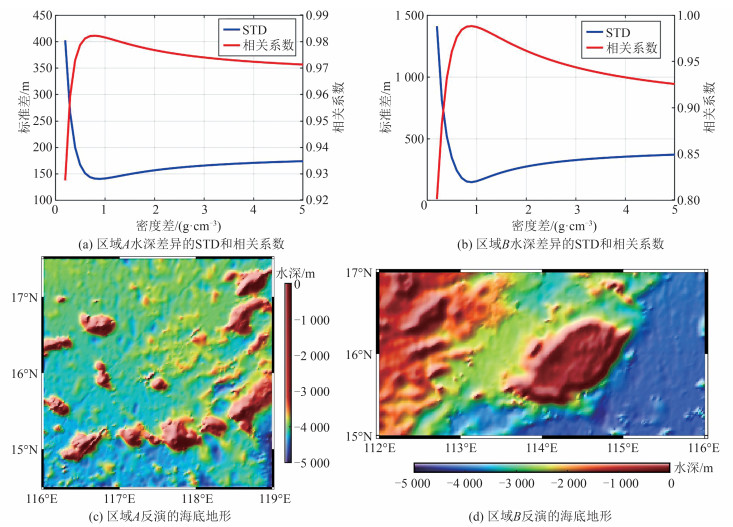
图 3是采用不同密度差获取的GGM反演结果与检核点水深差异的STD和相关系数。根据图 3(a),传统GGM反演结果与检核点水深较差的最小STD及最大相关系数对应的$ \Delta \rho =0.9\mathrm{ }\mathrm{g}/\mathrm{c}{\mathrm{m}}^{3} $,后文涉及传统GGM的计算均使用该密度差。根据图 3(b),改进GGM确定的最优$ \Delta \rho =1.1\mathrm{ }\mathrm{g}/\mathrm{c}{\mathrm{m}}^{3} $。对比图 3(a)、图 3(b)可知,两种方法对应的最优密度差略有差异,原因在于两种方法处理海底地形和重力间的关系时采用不同的假设。
2.3 海底地形反演
在GGM反演过程中,所构建的短波重力异常精度直接影响最终模型的精度。因此,定量分析海底地形非线性项对短波重力异常的贡献尤为重要。首先,将图 1所示的离散水深控制点在$ 1{'}\times 1{'} $的格网中求平均值,获得新的控制点。然后,利用GMT的surface模块,采用0.55张力的样条函数将新控制点格网化获得整个研究区的海底地形模型[23],下文称为SG模型,如图 4所示。由图 4可以看出,控制点直接网格化结果能反映研究区整体的地形变化,但在西北部大陆架和中沙群岛等地,由于船测数据稀缺,其地形十分粗糙且存在明显错误。
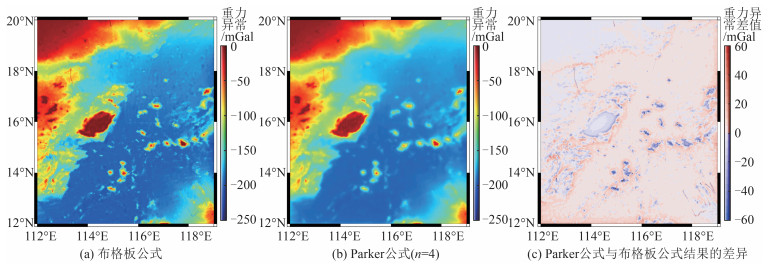
考虑到船测资料分布不均,本文采用SIO V23.1模型填充除控制点以外的格网值来构建初始模型,用于评估海底地形非线性项。图 5为利用布格板公式、Parker公式(式(7)中$ n=4 $[4],$ d=3\mathrm{ }164 $ m)正演初始模型获得的海面重力异常及二者差异。由图 5(a)、5(b)可以看出,受局部地形的影响,Parker公式计算结果相比布格板公式更为平滑。由图 5(c)可以看出,在平坦地区,非线性项影响接近于零,而在诸如海山链、岛屿和海盆边缘,非线性项的影响最高超过50 mGal。
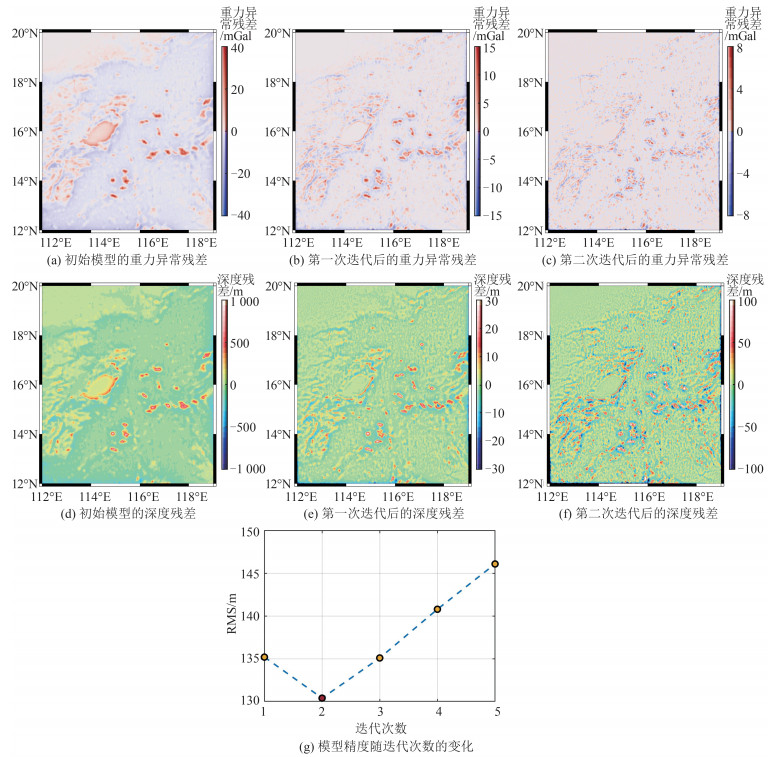
在获得控制点处的短波重力异常之后,首先采用三次卷积算法将测高重力异常格网插值到控制点上,计算控制点上的长波重力异常;然后,利用带张力的样条函数将长波重力异常格网化;最后,将测高重力异常格网减去长波重力异常格网获得用于海底地形反演的短波重力异常格网。进一步利用短波重力异常反演海底地形,采用改进GGM迭代反演过程如图 6所示。图 6(a)、6(b)和6(c)分别为初始模型、第一次迭代后和第二次迭代后的重力异常残差,计算其RMS分别为4.19 mGal、1.42 mGal和0.78 mGal。对应的深度残差分别如图 6(d)、6(e)和6(f)所示,计算其RMS分别为90.9 m、30.8 m和16.9 m。
由图 6(a)可知,仅考虑线性项会产生最大为40 mGal的重力残差,对应最大为1 000 m的深度残差(图 6(d))。第二次迭代后(图 6(b)),重力残差及深度残差均显著降低,重力残差RMS降至1.42 mGal,已低于测高重力异常的精度水平(2~3 mGal),反演模型与检核点间的RMS下降(图 6(g))。进一步迭代后(图 6(c)),虽然重力残差及深度残差仍在降低,最大深度残差降至100 m以下,但模型反演精度不降反升(图 6(g))。说明经过两次迭代后,重力残差已降至观测精度以下,在随后的迭代中,更多是将重力观测值噪声直接转化为水深,因而模型精度降低。综上所述,以重力观测值的精度水平作为迭代收敛条件较为合理。
由图 5可知,在利用Parker公式计算短波重力异常时,受周围地形引力的影响,控制点处的高频信息被平滑。为恢复控制点水深,计算反演模型与控制点水深的残差并将其格网化,再重新添加到重力反演模型中得到最终模型。为方便论述,后续将传统GGM反演结果称为GGM1模型,将改进GGM反演结果称为GGM2模型。
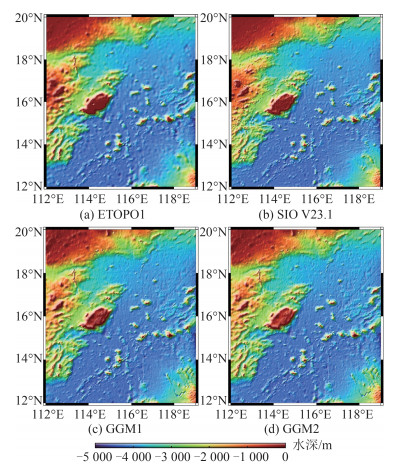
4种海底地形模型如图 7所示。由图 7可以看出,4种海底地形模型的整体趋势相同,南海海盆内除中部海山链外,以海底平原为主,地形平缓,水深在3 500~5 000 m。西北大陆架及中沙群岛附近的区域,地貌复杂,地形坡度大,水深在0~3 000 m范围内变化。对比ETOPO1模型及其他模型可以看出,ETOPO1模型的精细程度明显低于其他模型。GGM1模型与GGM2模型在形态上无明显区别,在研究区西部及西北部(113°E,17°N)附近,GGM类模型的精细程度不如SIO V23.1模型,主要原因是此处的船测水深数据分布稀疏。
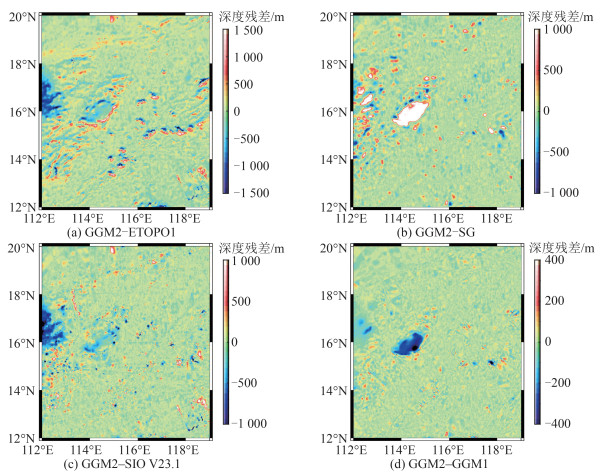
图 8为GGM2模型与其他模型的差异。由图 8(a)、图 7(a)和7(d)可以看出,GGM2模型与ETOPO1存在明显差异,主要位于海山链、岛屿群和地形变化梯度带上,其主要源于GGM2模型精细度的提高。由图 8(b)可以看出,GGM2模型与SG(Savitzky-Golay)模型的差异集中于中沙群岛及其西部,归因于船测资料匮乏。由图 8(c)可以看出,GGM2模型与SIO V23.1模型间的差异多数沿船测线分布,这主要与所采用的船测数据质量、处理及融合技术不同有关。由图 8(d)可以看出,GGM2与GGM1模型整体差异不大,中沙群岛处的明显差异源于GGM2使用了SIO V23.1模型作为填充,其余差异多集中于局部地形起伏较大的地区,反映了海底地形的非线性项信息。
2.4 模型精度分析
利用检核点评估各海底地形模型的精度,结果如表 1所示。表 1中的相对误差被定义为模型在所有检核点上的水深偏差与相应检核点水深之比的绝对值取平均值[24]。由表 1可以看出,SG模型精度最低,其RMS为255.4 m,相对误差高达6.24%,平均偏差为-26.0 m,表明其与检核点间存在系统偏差。ETOPO1模型的精度亦明显低于SIO V23.1模型、GGM1模型和GGM2模型,其RMS为167.5 m,同样存在较大的系统偏差。SIO V23.1、GGM1和GGM2模型精度相当,GGM2模型精度略优于GGM1模型,精度提升2.8 m,且平均偏差最小,为-2.9 m。从相对误差分析,SIO V23.1模型最优,仅为3.09%;其次是GGM2模型,为3.83%,略优于GGM1模型。
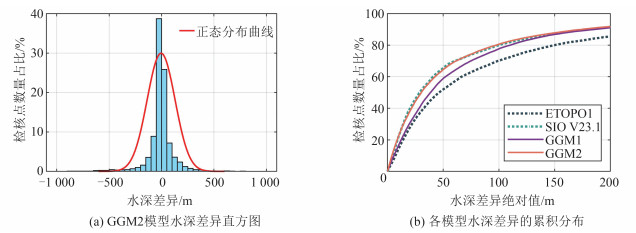
表 1 各海底地形模型与检核点差异Table 1. Deviations Between Various Seafloor Topography Models and Check Points模型 最大值/m 最小值/m 平均值/m 标准差/m RMS/m 相对误差/% ETOPO1 1 056.8 -1 537.4 -21.48 166.1 167.5 4.39 SIO V23.1 1 354.1 -1 169.1 14.4 143.4 144.1 3.09 SG 1 095.0 -2 816.5 —26.0 254.1 255.4 6.24 GGM1 1 118.6 -1 698.6 -4.3 133.2 133.2 3.90 GGM2 1 110.0 -1 526.4 -2.9 130.4 130.4 3.83 图 9(a)为GGM2模型水深差异直方图,条块宽度为50 m。由图 9(a)可以看出,大多数水深差异集中在±100 m范围内,与正态分布相比,具有更尖锐的“山峰”和更长的“尾部”。图 9(b)为各模型水深差异的累积分布。ETOPO1、SIO V23.1、GGM1和GGM2模型水深差异绝对值在100 m以内的检核点数占比分别为70.2%、80.0%、77.7%和77.1%。
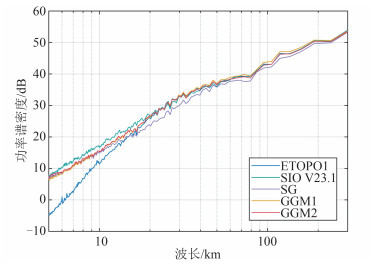
为了进一步考察各模型在不同波长上的表现,计算各模型的径向功率谱密度,结果如图 10所示。其中,纵轴进行了10lg缩放。由图 10可知,波长小于20 km时,SIO V23.1模型具有最高的能量,且明显优于其他模型。随后,GGM2模型的能量略高于SG和GGM1模型。ETOPO1模型在短波长中的能量远低于其他模型。出现上述现象的主要原因是,在小于20 km波段内,测高重力异常的信噪比较低,海底地形与重力异常间的相干性不高[3],因而该波段海底地形信号主要来源于船测水深。最新的SIO V23.1模型所基于的船测数据质量可能更优,从而使其具有更高的能量;SG、GGM1和GGM2模型采用相同的船测水深控制点,因而具有相同的能谱;ETOPO1模型于2008年发布,其融合的船测资料最小,所以表现最差。在20~130 km的中长波段内,除SG模型曲线明显偏低外,其他模型表现较为接近。该波段是重力数据的主要贡献区间[3],未使用重力数据的SG模型应具有最低的能量。值得注意的是,在大于80 km波段内,GGM1模型的能谱略高于其他模型,其原因有待进一步研究。
为分析各模型精度与水深之间的关系,统计不同水深范围内各模型与检核点差异的RMS,见表 2。由表 2可知,在深度小于1 000 m的浅水区,SIO V23.1模型精度优于GGM1和GGM2模型,3种模型的RMS分别为61.1 m、117.6 m和119.9 m,表明GGM法反演浅水区海底地形并无优势。GGM法的优势水深区间位于[1 000,2 000)m、[3 000,4 000)m及≥4 000 m的深水区,在上述区间内,GGM1和GGM2模型精度均显著优于SIO V23.1模型。此外,GGM2相比与GGM1模型在1 000~4 000 m区间内精度更高,提升了5~10 m。
表 2 各海底地形模型与检核点差异的RMSTable 2. RMS of Deviation Between Various Seafloor Topography Models and Check Points水深区间/m 检核点数量/个 RMS/m SIO V23.1 GGM1 GGM2 < 1 000 2 170 61.1 117.6 119.9 [1 000, 2 000) 2 135 230.1 175.7 166.1 [2 000~3 000) 2 454 167.7 194.3 191.3 [3 000~4 000) 8 150 173.1 160.9 155.9 ≥4 000 11 076 97.3 74.5 75.9 许多研究表明,应用GGM反演大范围复杂地区的海底地形时,有必要按地质条件区分各子区以采用不同的密度差进行反演[16, 24]。为了客观分析GGM2模型在复杂地形区的性能,本文分别反演了区域A(116°E~119°E,14.5°N~17.5°N)和区域B(112°E~116°E,15°N~17°N)的海底地形,并计算了不同密度差反演结果与检核点水深差异的STD和相关系数,结果如图 11所示。各模型在2个区域与检核点的比较统计见表 3。
表 3 不同海底地形模型与A、B区域检核点比较Table 3. Comparison Between Various Seafloor Topography Models and Check Points in Areas A and B区域 检核点数量/个 模型 最大值/m 最小值/m 平均值/m 标准差/m RMS/m 相对误差/% A 3 767 ETOPO1 1 020.7 -1 537.4 -15.6 213.2 213.7 4.40 SIO V23.1 853.2 -584.0 12.0 106.1 106.8 2.11 GGM1 1 125.7 -1 680.6 -11.0 151.5 151.8 3.00 GGM2 947.9 -1 461.0 -8.9 140.7 141.0 2.91 B 5 511 ETOPO1 644.1 -1 053.3 -53.6 202.9 209.9 5.95 SIO V23.1 1 354.1 -868.1 47.1 219.7 224.7 4.54 GGM1 522.0 -937.9 -31.2 151.8 154.9 4.20 GGM2 509.4 -908.3 -25.1 148.1 150.2 4.14 区域A内包含黄岩海山链及众多海丘,地形变化复杂,但具有均匀分布的船测水深数据。由图 11(a)可知,区域A确定的$ \Delta \rho =0.9\mathrm{ }\mathrm{g}/\mathrm{c}{\mathrm{m}}^{3} $;由表 3可知,区域A中SIO V23.1模型具有最高精度,其RMS为106.8 m;ETOPO1模型精度最差,GGM类模型精度远优于ETOPO1模型,不如SIO V23.1模型。GGM2模型的RMS为141.0 m,相比GGM1模型精度提升了10.8 m,该结果表明,在复杂地形区GGM反演中,考虑地形非线性项能有效提高模型精度。
区域B中部为中沙群岛,西部为西沙群岛东侧,存在众多岛礁和海沟、海槽,东部向南海海盆过渡,地形坡度大。此外,该区域的船测数据匮乏,会影响海底地形反演的质量。由图 11(b)可知,区域B确定的$ \Delta \rho =0.9\mathrm{ }\mathrm{g}/\mathrm{c}{\mathrm{m}}^{3} $;从表 3可知,区域B中GGM2模型具有最高的精度,其RMS为150.2 m,相对误差4.14%,相比GGM1模型精度提升了4.7 m;SIO V23.1模型的RMS最大,ETOPO1模型的相对误差最高。
3 结语
针对传统GGM方法仅顾及地形线性部分而忽略非线性项的问题,本文利用频率域重力正演方法和迭代缩放技术来恢复海底地形的非线性信息,生成了中国南海1'×1'海底地形模型,并对模型的精度水平进行了综合评估。结果表明:
1)仅使用简单布格板公式计算的短波重力异常与四阶Parker公式计算结果相比会引起超过50 mGal的偏差,尤其是在地形起伏较大的地区。
2)应用迭代缩放技术并以观测重力异常的精度水平作为收敛条件,能改善从短波重力异常中所恢复海底地形的质量。
3)与ETOPO1和SIO V23.1模型相比,由改进GGM反演得到的GGM2模型在研究区中具有最高的精度,它与检核点差异的RMS为130.4 m;平均值为-2.9 m;相对误差等于3.83%。GGM2模型相对于由传统GGM获得的GGM1模型,精度提升2.8 m,主要获得改善的水深区间为1 000~4 000 m。
4)分区反演结果表明,改进GGM相比传统GGM在黄岩海山链附近改善效果较好,精度提高了10.8 m;在中沙群岛附近精度提高了4.7 m。
-
表 1 各海底地形模型与检核点差异
Table 1 Deviations Between Various Seafloor Topography Models and Check Points
模型 最大值/m 最小值/m 平均值/m 标准差/m RMS/m 相对误差/% ETOPO1 1 056.8 -1 537.4 -21.48 166.1 167.5 4.39 SIO V23.1 1 354.1 -1 169.1 14.4 143.4 144.1 3.09 SG 1 095.0 -2 816.5 —26.0 254.1 255.4 6.24 GGM1 1 118.6 -1 698.6 -4.3 133.2 133.2 3.90 GGM2 1 110.0 -1 526.4 -2.9 130.4 130.4 3.83 表 2 各海底地形模型与检核点差异的RMS
Table 2 RMS of Deviation Between Various Seafloor Topography Models and Check Points
水深区间/m 检核点数量/个 RMS/m SIO V23.1 GGM1 GGM2 < 1 000 2 170 61.1 117.6 119.9 [1 000, 2 000) 2 135 230.1 175.7 166.1 [2 000~3 000) 2 454 167.7 194.3 191.3 [3 000~4 000) 8 150 173.1 160.9 155.9 ≥4 000 11 076 97.3 74.5 75.9 表 3 不同海底地形模型与A、B区域检核点比较
Table 3 Comparison Between Various Seafloor Topography Models and Check Points in Areas A and B
区域 检核点数量/个 模型 最大值/m 最小值/m 平均值/m 标准差/m RMS/m 相对误差/% A 3 767 ETOPO1 1 020.7 -1 537.4 -15.6 213.2 213.7 4.40 SIO V23.1 853.2 -584.0 12.0 106.1 106.8 2.11 GGM1 1 125.7 -1 680.6 -11.0 151.5 151.8 3.00 GGM2 947.9 -1 461.0 -8.9 140.7 141.0 2.91 B 5 511 ETOPO1 644.1 -1 053.3 -53.6 202.9 209.9 5.95 SIO V23.1 1 354.1 -868.1 47.1 219.7 224.7 4.54 GGM1 522.0 -937.9 -31.2 151.8 154.9 4.20 GGM2 509.4 -908.3 -25.1 148.1 150.2 4.14 -
[1] Smith W. Introduction to this Special Issue on Bathymetry from Space[J]. Oceanography, 2004, 17(1): 6-7. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2004.62
[2] Sandwell D, Garcia E, Soofi K, et al. Toward 1-mGal Accuracy in Global Marine Gravity from CryoSat-2, Envisat, and Jason-1[J]. The Leading Edge, 2013, 32(8): 892-899. doi: 10.1190/tle32080892.1
[3] Smith W H F, Sandwell D T. Global Sea Floor Topography from Satellite Altimetry and Ship Depth Soundings[J]. Science, 1997, 277(5334): 1956-1962. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5334.1956
[4] 范雕, 李姗姗, 孟书宇, 等. 海底地形高次项对海面重力信息影响分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(9): 1328-1335. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190192 Fan Diao, Li Shanshan, Meng Shuyu, et al. Influence Analysis of High-Order Seafloor Topography on Sea Surface Gravity Information[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(9): 1328-1335. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190192
[5] Ramillien G, Wright I C. Predicted Seafloor Topo-graphy of the New Zealand Region: A Nonlinear Least Squares Inversion of Satellite Altimetry Data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2000, 105(B7): 16577-16590. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900099
[6] Kim K B, Hsiao Y S, Kim J W, et al. Bathymetry Enhancement by Altimetry-Derived Gravity Anomalies in the East Sea (Sea of Japan)[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2010, 31(4): 285-298. doi: 10.1007/s11001-010-9110-0
[7] Kim J W, Frese R R B, Lee B Y, et al. Altimetry-Derived Gravity Predictions of Bathymetry by the Gravity-Geologic Method[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2011, 168(5): 815-826. doi: 10.1007/s00024-010-0170-5
[8] Hsiao Y S, Kim J W, Kim K B, et al. Bathymetry Estimation Using the Gravity-Geologic Method: An Investigation of Density Contrast Predicted by the Downward Continuation Method[J]. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 2011, 22(3): 347. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2010.10.13.01(Oc)
[9] Xiang X S, Wan X Y, Zhang R N, et al. Bathymetry Inversion with the Gravity-Geologic Method: A Study of Long-Wavelength Gravity Modeling Based on Adaptive Mesh[J]. Marine Geodesy, 2017, 40(5): 329-340. doi: 10.1080/01490419.2017.1335257
[10] Sun Y J, Zheng W, Li Z W, et al. Improved the Accuracy of Seafloor Topography from Altimetry-Derived Gravity by the Topography Constraint Factor Weight Optimization Method[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(12): 2277. doi: 10.3390/rs13122277
[11] Xing J, Chen X X, Ma L. Bathymetry Inversion Using the Modified Gravity-Geologic Method: Application of the Rectangular Prism Model and Tikhonov Regularization[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2020, 17(3): 377-389. doi: 10.1007/s11770-020-0821-y
[12] 欧阳明达, 孙中苗, 翟振和. 基于重力地质法的南中国海海底地形反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(9): 2756-2765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201409004.htm Ouyang Mingda, Sun Zhongmiao, Zhai Zhenhe. Predicting Bathymetry in South China Sea Using the Gravity-Geologic Method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(9): 2756-2765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201409004.htm
[13] Yang J J, Jekeli C, Liu L T. Seafloor Topography Estimation from Gravity Gradients Using Simulated Annealing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123: 6958-6975.
[14] Ibrahim A, Hinze W J. Mapping Buried Bedrock Topography with Gravity[J]. Ground Water, 1972, 10(3): 18-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1972.tb02921.x
[15] Kim K B, Yun H S. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Prediction in Shallow Waters Using the Gravity-Geologic Method: A Case Study in the West Sea of Korea[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2018, 22(7): 2560-2568. doi: 10.1007/s12205-017-0487-z
[16] Annan R F, Wan X Y. Mapping Seafloor Topography of Gulf of Guinea Using an Adaptive Meshed Gravity-Geologic Method[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2020, 13(7): 1-12.
[17] 胡敏章, 李建成, 金涛勇. 顾及局部地形改正的GGM海底地形反演[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2013, 38(1): 60-63. http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/6073 Hu Minzhang, Li Jiancheng, Jin Taoyong. Bathymetry Prediction from GGM Method with Terrain Reductions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2013, 38(1): 60-63. http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/6073
[18] Parker R L. The Rapid Calculation of Potential Anomalies[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1973, 31(4): 447-455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1973.tb06513.x
[19] Fan D, Li S S, Li X X, et al. Seafloor Topography Estimation from Gravity Anomaly and Vertical Gravity Gradient Using Nonlinear Iterative Least Square Method[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 13(1): 64. doi: 10.3390/rs13010064
[20] Silva J B C, Santos D F, Gomes K P. Fast Gravity Inversion of Basement Relief[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(5): G79-G91. doi: 10.1190/geo2014-0024.1
[21] Tozer B, Sandwell D T, Smith W H F, et al. Glo-bal Bathymetry and Topography at 15 Arc Sec: SRTM15+[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2019, 6(10): 1847-1864. doi: 10.1029/2019EA000658
[22] Amante C. ETOPO1 1 Arc-Minute Global Relief Model : Procedures, Data Sources and Analysis[R]. Washington: National Geophysical Data Center, 2009.
[23] Smith W H F, Wessel P. Gridding with Continuous Curvature Splines in Tension[J]. Geophysics, 1990, 55(3): 293-305. doi: 10.1190/1.1442837
[24] Wei Z J, Guo J Y, Zhu C C, et al. Evaluating Accuracy of HY-2A/GM-Derived Gravity Data with the Gravity-Geologic Method to Predict Bathymetry[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 636246.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 欧阳明达,翟振和,牛向华,管斌,张鹏飞,付永健. 基于神经网络的船测稀疏海域地形反演改进算法. 中国惯性技术学报. 2025(01): 64-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 公维梁,屠泽杰,孙月文,邢赛,赵福玺,阳凡林. 一种基于重力正演理论的海底地形反演迭代算法. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(03): 64-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杜斌,范雕,胡兴猛,谭勖立,万宏发,裴宪勇. 基于重力异常数据构建海陆交界区域海底地形模型. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2024(08): 873-880 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: