On the Accuracy and PPP Performance Evaluation of the Latest Generation of Real Time Tropospheric Mapping Function
-
摘要: 采用射线追踪方法计算的斜路径总延迟(slant total delay,STD)作为参考,首先评估了最新一代实时对流层映射函数GPT3 (global pressure and temperature 3)、格网VMF3-FC(forecast Vienna mapping function 3)和站处VMF3-FC的STD建模精度,然后将3种映射函数用于北斗三号(BDS3)精密单点定位(precise point positioning,PPP),系统比较了3种映射函数计算的PPP坐标精度。结果表明,站处VMF3-FC 30°高度角时STD精度为2.3 cm,BDS3 PPP高程精度为9.8 mm,整体表现最优,推荐在有站处产品的IGS(international GNSS service)站处使用该映射函数产品;格网VMF3-FC 30°高度角STD精度为2.6 cm,BDS3 PPP高程精度为10.2 mm,整体表现次之,在无站处产品的情况下推荐使用;GPT3 30°高度角STD精度为7.0 cm,BDS3 PPP高程精度为10.5 mm,整体表现最差,但其可内嵌在定位软件中,在无需下载外部产品的情况下推荐使用。Abstract:Objectives Real-time tropospheric mapping functions can be used into real time global navigation satellite system (GNSS) parameter estimation and applications, and it is therefore of great significance to evaluate their modeling accuracy and precise point positioning (PPP) performance.Methods In this paper, the slant total delay (STD) modeling accuracy of the latest generation of real time mapping functions, including global pressure and temperature 3 (GPT3), grid-wise forecast vienna mapping function 3 (VMF3-FC) and site-wise VMF3-FC, is evaluated by taking ray-traced STD as a reference, and the BDS3 PPP performance of the three mapping functions is analyzed on the coordinate accuracy.Results The results show that the site-wise VMF3-FC persists the best performance with STD accuracy of 2.3 cm at the 30° elevation angle and BDS3 PPP height accuracy of 9.8 mm, and it is recommended to use at the international GNSS service(IGS) stations with the site-wise products. The performance of the grid-wise VMF3-FC is a little worse with the STD accuracy of 2.6 cm and height accuracy of 10.2 mm, and it is recommended as the backup of the site-wise VMF3-FC products. The GPT3 model has the worst performance with the STD accuracy of 7.0 cm and height accuracy of 10.5 mm, while it can be embedded into the positioning software, so it is recommended to use in the case of without the need of external products.
-
Keywords:
- real-time mapping function /
- VMF3-FC /
- GPT3 /
- BDS3-PPP
-
随着中国经济的飞速发展,工业、交通也迅猛发展,城市扩张,人口集中,各种环境问题也层出不穷,其中大气污染,尤其是颗粒物(气溶胶)污染具有广泛的空间分布,对人体健康产生较大危害[1]。空气动力学当量直径小于10 μm的颗粒物被称为PM10,直径小于2.5 μm的颗粒物被称为PM2.5,二者均具有可吸入性,前者通常可以沉积到上呼吸道,而后者可以进入肺泡,对身体危害极大;同时细颗粒物在大气中停留时间长,也影响了大气能见度和大气环境质量[1-3]。
在颗粒物污染监测中,近地表的监测备受人们关注,各个城市中普遍设立了空气质量监测站,同时监测颗粒物浓度(PM10、PM2.5)、硫氧化物、氮氧化物等参数,能够测量站点附近大气污染的详细参数,测量精度高,但受制于成本,不能广泛布站,覆盖区域的测量很难实现,无法全面反映气溶胶的分布。激光雷达作为一种遥感手段,能够进行长距离、高频次的探测,探测结果可以有效反映激光传输路径内的气溶胶分布情况,是当前遥感探测颗粒物污染的有效手段,被广泛应用于城市大气污染探测中[4-11]。国内外多家单位开展了激光雷达用于大气探测的研究,其中中科院安光所[4-7]、武汉大学[8]、西安理工大学[9]等多家国内单位,以及法国索邦大学[10]、日本国立环境研究所[11-12]、意大利[13]、美国NOAA[14]等国外研究机构均利用激光雷达进行了颗粒物探测。
当前国内外的研究中,都是单独进行垂直探测[1, 5, 8-10, 12-17]或者水平探测[4, 6-7],鲜有结合三维探测的激光雷达数据进行相关研究。垂直探测可以确定探测地点上空的气团垂直分布和运动,但是不能获得区域性的颗粒物分布;水平探测可用于识别该区域的颗粒物水平分布,但牺牲了时间分辨率,无法获得颗粒物的传输规律;而同时结合垂直和水平探测组成的三维数据,即可实现两种探测方式的优势互补,从而实现对颗粒物更全面的监测和研究。本文即利用两台微脉冲激光雷达对天津市武清区中心城区进行了全天时的遥感探测,其中一台激光雷达进行垂直测量,探测颗粒物的传输、沉降;另外一台激光雷达架设于高楼顶,进行水平扫描,探测颗粒物的水平分布。通过对两台激光雷达的三维数据的分析,揭示区域性的颗粒物污染分布和传输情况。
1 三维大气污染探测原理与方法
1.1 大气探测激光雷达原理
激光雷达是一种主动探测设备,它向大气中发射激光脉冲,激光束与大气气溶胶粒子和大气分子等发生相互作用,产生回波信号被接收望远镜接收,然后对回波信号进行采集、反演就可以得到大气气溶胶的光学特征信息。激光雷达探测大气颗粒物具有很高的空间和时间分辨率,是目前有效获得大气颗粒物垂直分布廓线的重要手段。
1.2 实验方法和研究区域介绍
本文研究中为了获取大气颗粒物的三维数据,同时采用了两台激光雷达分别进行大气垂直和水平扫描探测。垂直探测和水平扫描激光雷达的技术指标如表 1所示。在大气激光雷达探测中一般采用的是Nd:YAG激光器的基频光,即1 064 nm,因此本文采用的激光雷达的激光波长均为1 064 nm。同时对激光雷达进行了一体化设计,并加入窄带滤光片,使得其具有全天时、全天候工作能力,从而实现24 h连续监测。
表 1 激光雷达技术参数Table 1. Parameters of the Two LiDARs参数 垂直LiDAR 水平LiDAR 波长/nm 1 064 1 064 能量/μJ >100 >20 脉冲频率/kHz 1 1 望远镜口径/ mm 100 100 距离分辨率/m 30 15 滤光片带宽/nm 0.5 0.5 激光雷达的布设区域选择在天津市武清区城区。武清城区处于京津冀的中心地带,其大气颗粒物污染受外地源影响较为明显,希望通过激光雷达遥感探测的手段找出污染的传输方向,并初步判定污染源。垂直探测激光雷达和水平探测激光雷达分别部署于同一小区中不同建筑楼顶,为保证水平探测路径内无遮挡,将水平探测激光雷达部署于城区内的一栋33层居民楼楼顶,具体地理位置在水平扫描结果中可见。
1.3 垂直探测激光雷达反演算法
大气探测激光雷达信号反演中一般采用Fernald算法[18],该算法主要是区分了大气气溶胶和大气分子,并引入激光雷达比的概念,进行大气气溶胶消光系数和后向散射系数的计算。具体如下:
$$ {P(r) = EC{r^{ - 2}}\beta (r)\exp \left[ { - 2\int_0^r \sigma (r){\rm{d}}r} \right]} $$ (1) $$ {{S_1} = {\sigma _1}(r)/{\beta _1}(r)} $$ (2) $$ {{S_2} = {\sigma _2}(r)/{\beta _2}(r)} $$ (3) $$ \begin{array}{l} {\sigma _1}(I - 1) + \frac{{{S_1}}}{{{S_2}}}{\sigma _2}(I - 1) = X(I - 1) \times \\ \exp [ + A(I - 1, I)]/\left\{ {\frac{{X(I)}}{{{\sigma _1}(I) + \left( {{S_1}/{S_2}} \right){\sigma _2}(I)}} + } \right.\\ X(I)\Delta r + X(I - 1)\exp [ + A(I - 1, I)]\Delta r\} \end{array} $$ (4) 式(1)为典型的大气激光雷达方程,是大气颗粒物探测的基本方程,所有利用激光雷达进行大气探测均是基于该方程进行的,其中,P为激光雷达回波信号强度功率;r代表探测距离;E为激光雷达固定参数,包括发射激光功率等;C为矫正常数;β为大气后向散射系数;σ为大气消光系数。式(2)和式(3)分别是大气气溶胶和大气分子的激光雷达比计算方程,是Fernald算法的核心,其中S1和S2分别是大气气溶胶和大气分子的激光雷达比;大气分子的激光雷达比为固定值8π/3,下标1表示大气颗粒物/气溶胶,下标2表示大气分子。式(4)为利用Fernald算法进行消光系数的后向积分方程,其中I代表高度相关的计数值。
通过确定激光雷达比、标定高度和标定高度处的大气气溶胶消光系数3个参数后,即可以利用Fernald算法进行气溶胶消光系数的计算。其中激光雷达比一般采用定值简化计算,本文设定为50;标定高度选择在相对洁净、大气气溶胶少的区域,本文选择高度10 km为标定高度rc,该处的气溶胶消光系数计算采用经验公式a1(rc)=(1.01-1)a2(rc)计算[18],其中分子的消光系数由大气模式给出。
1.4 水平扫描激光雷达反演算法
水平扫描激光雷达信号处理算法是在垂直探测算法的基础上完成的。目前一般采用的是斜率法或者Fernald法,但前者的问题在于其假定的大气分布均匀状态在实际情况下不成立,而后者的弊端在于无法获得标定高度(距离)及在此处的气溶胶消光系数[18-21]。
为减小反演误差,本文结合斜率法和Fernald算法,提出了一种新的水平扫描反演算法。斜率法不存在激光雷达比的问题,但水平方向上某小段距离内可以认为大气状态均匀,在本次实验中,先根据原始激光雷达信号确定大气分布均匀的一段距离,并以斜率法获取该处的气溶胶平均消光系数,将结果作为Fernald算法的标定高度(距离)和此处的消光系数标定值。
由于获取的是中间距离的消光系数,因此利用Fernald算法时,分别进行前向和后向积分,从而得到较为准确的大气气溶胶消光系数反演结果。
2 三维大气污染探测实验与结果分析
本文选取2018年7月16日水平和垂直激光雷达数据进行反演,揭示该地区的颗粒物三维分布特征,并同地面空气质量国控站点的PM数据进行校正和对比分析。
2.1 垂直探测结果分析
对7月16日连续24 h的垂直探测结果,利用Fernald算法进行反演,标定高度选为10 km,图 1(a)为2018年7月16日凌晨00:30时刻的单条垂直激光雷达距离校正信号,可以看出激光传输距离较远,表明高层大气较为洁净,在高度0.5 km附近,信号强度先增加后减小是由于overlap效应造成的,即激光没有完全进入望远镜视场;在高度2.5 km处,激光雷达回波信号出现突增现象,表明此处有明显的云层,但厚度较薄,穿过云层后激光的衰减较小,继续传输至高空中。
图 1(b)是7月16日连续24 h垂直探测得到的大气气溶胶消光系数,通过消光系数可以直接反映出大气气溶胶的浓度情况,其中高度2.5 km处的消光系数出现极大值,是由于云层造成的,不在本文的研究范围内。
一般情况下,气溶胶主要集中在边界层内,由于探测时间为夏天,边界层高度较高,利于污染物扩散。根据查询到的气象数据,激光雷达探测从0时至早上8时左右,边界层以下的颗粒物浓度较低,且呈逐渐消散(扩散)的趋势;但从早上8时左右开始,上午低空的气溶胶消光系数持续增加,可以看出,颗粒物污染也持续增加,表明当地的人为颗粒物排放较为严重,同时颗粒物由低空向高空传输的特征明显,因此可以判定当天的大气气溶胶污染主要是本地源,即从地面向高空扩散;白天污染持续增加,到夜晚24时达到顶峰,这一现象主要是人为活动造成的。武清区是天津和北京的交界处,该处白天和夜晚的交通活动较强,同时夜晚气溶胶浓度持续增加的主要原因不排除当地企业夜间生产偷排的情况。
2.2 水平扫描结果分析
通过布设在居民楼顶的水平扫描激光雷达(117.04°E,39.39°N)探测气溶胶在水平方向上的分布。为了保证信噪比,将单次扫描角度时间设置为20 s,扫描步进角度为2°,水平方向顺时针扫描一圈时间为1 h。利用本文提出的水平反演算法进行了消光系数反演,图 2(a)为7月16日凌晨00:30激光雷达单次扫描得到的距离校正信号,同图 1(a)相比,水平探测中,由于地表附近较高空气溶胶浓度高,因此回波信号随距离增加而衰减的程度较大;同时由于水平气溶胶分布的不均匀性,水平探测的回波信号波动也较大,采用斜率法进行反演会造成一定的反演误差。
图 2(b)为水平方向上1 h(16日凌晨00:25-01:25)探测得到的大气气溶胶消光系数分布图,其中A为激光雷达站点位置,图中消光系数较大的区域气溶胶浓度较高,此段时间内污染集中在以探测点为中心的主城区内,以及南部高铁站附近。由于是凌晨,气溶胶污染主要集中在城区附近,人口密度高,与生产、生活、交通的污染排放有关,而郊区的人类活动和生产较少,污染较低。
图 2(c)为一天24 h连续探测后的数据融合结果,反映24 h内区域中的污染较大区域分布。采取的方法是提取高污染区域的颗粒物数据,剔除低污染部分,并融合到一张图中。可以看出,当天24 h内共有8个污染较重的区域,标号3~8的污染区域主要集中在城区中,表明城区人为活动是造成颗粒物污染的主要原因;1号、2号区域位于远城区,人类活动较少,但实际污染程度也较大,根据实地调查,两处地区有本地工厂,工业活动是造成该区域气溶胶浓度上升的主要原因。
根据垂直激光雷达探测的结果,如图 1(a)所示,可知当天气溶胶污染源主要是本地源,结合图 2(c),充分表明在本地污染源起主导作用的情况下,大气气溶胶污染主要集中在城区部分;同时结合图 2(b)可知,城区地区发达的交通和密集的人口加重了武清区的夜间污染,且密集的建筑物使得气溶胶扩散不易。
3 讨论
需要说明的是,激光雷达探测反演得到的颗粒物消光系数是相对值,可以在一定程度上反映出观测区域中的颗粒物浓度情况,一般情况下,这种探测结果结合地面国控站数据即可实现区域内的颗粒物密集监测,但无法直接将颗粒物的消光系数转换到绝对的颗粒物浓度值。研究表明,颗粒物浓度同激光雷达探测得到的消光系数间存在一定的线性关系,尤其是颗粒物消光系数和PM10之间的线性关系更为明显。因此在完成垂直和水平激光雷达探测实验后,为初步验证激光雷达探测结果的准确性,将激光雷达水平扫描结果同地面站点数据进行对比,地面站点数据采用的是扫描区域内的国控站点PM10数据。
需要指出的是,由于激光雷达是位于高点处进行扫描的,其探测结果同地面国控站点间必定存在一定的偏差,因此在进行相关性计算时,需要考虑到当天的风速和风向,若风速较大,需要以下风处的气溶胶消光系数平均值作为对比值,为了降低对比误差,本文此次选取了风速较低的情况下的数据。
图 3是激光雷达探测到的气溶胶消光系数同PM10间的相关性对比,由于水平激光雷达数据获取周期为1 h,因此对国控站的PM10数据进行小时平均,采用223组对比数据,即近10 d的数据,拟合得到的颗粒物消光系数反演PM10浓度的经验公式为:y=767.82x+10.08,R2为0.85,表明二者间的线性关系较为明显,即颗粒物的消光系数可以转换为精度较高的颗粒物浓度数据。若通过长期数据积累,可以得到更为准确的经验公式。
通过上述实际数据对比分析,可以认为气溶胶消光系数和颗粒物浓度(尤其是PM10)间的线性程度较高,因此,在获取一定时间内的经验公式后,可以利用激光雷达探测到的气溶胶消光系数的水平分布图,直接反映扫描区域内颗粒物浓度的分布情况。
4 结语
本文利用两台激光雷达分别进行垂直方向和水平扫描探测,获得了区域性的气溶胶三维分布结果。其中利用垂直探测得到气溶胶的垂直分布,并说明一天24 h内边界层高度变化下低层大气气溶胶的扩散情况,初步揭示当天的气溶胶污染源是本地或是外地;同时利用布设在高楼顶的水平扫描激光雷达获取气溶胶的水平分布结果,探明扫描区域内的气溶胶污染分布情况。三维数据的激光雷达相比于传统的被动站点布设,能以更少的成本反映区域的气溶胶分布情况以及变化趋势,为城市颗粒物监测和治理提供了有效的测量手段。
需要指出的是,单独的激光雷达只能对区域气溶胶进行实时监测,若加上偏振通道,则可以区分本地和外源沙尘性气溶胶,但仍然无法实现对污染物的溯源、预测。而卫星遥感手段能够对大尺度的PM2.5、PM10进行监测,结合气象数据,构建后向轨迹模型,追溯气团运动轨迹,可以实现对颗粒物污染的追踪和预测,这也是下一步需要完善的工作。
致谢: 本文实验所需的数据产品由IGS、GFZ、ECMWF和维也纳工业大学提供,数值计算得到武汉大学超级计算中心的计算支持和帮助,在此一并表示感谢。 -
表 1 3种映射函数的斜路径总延迟建模RMS统计/cm
Table 1 Statistical Slant Total Delay RMS for Three Mapping Functions/cm
模型产品 高度角 3° 5° 7° 10° 15° 30° 70° 90° GPT3 53.7 36.3 27.1 19.6 13.3 7.0 3.7 3.5 VMF3-FC-G 20.4 13.8 10.2 7.4 5.0 2.6 1.4 1.3 VMF3-FC-S 17.2 11.7 8.7 6.3 4.3 2.3 1.2 1.1 项目 处理策略 处理采样间隔/s 30 观测值 无电离层组合观测值:
BDS3-B1I、B3I组合
GPS-L1、L2组合截止高度角/(°) 3 高度角加权策略 天线相位缠绕 改正 相位中心变化 igs14.atx 潮汐改正 固体潮、极潮、海洋潮 相对论效应 改正 先验STD 1 ZHD: SAAS[18]+ GPT3
ZWD: 文献[19]+ GPT3
映射函数:GPT3先验STD 2 ZHD和ZWD:VMF3-FC-G
映射函数:VMF3-FC-G先验STD 3 ZHD和ZWD:VMF3-FC-S
映射函数:VMF3-FC-S卫星轨道 固定到GBM 5 min产品 卫星钟差 固定到GBM 30 s产品 湿映射函数1 GPT3 湿映射函数2 VMF3-FC-G 湿映射函数3 VMF3-FC-S 残余ZWD 分段常数(1 h)+段间随机游走( ) 梯度映射函数 [ 32 ]水平梯度 分段常数(12 h)+段间随机游走(10 mm/ ) 测站坐标 天常数 接收机钟差 白噪声 模糊度参数 固定 表 3 不同季节下3种映射函数的BDS3和GPS PPP坐标重复性/mm
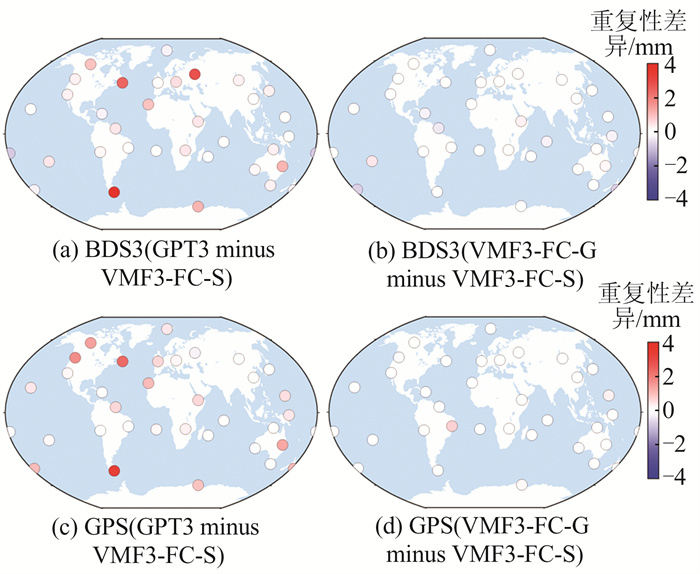
Table 3 BDS3 and GPS PPP Coordinate Repeatability for the Three Mapping Functions During Different Seasons/mm
季节 模型产品 BDS3坐标重复性 GPS坐标重复性 E N U E N U 冬季 GPT3 3.5 2.3 6.4 1.7 1.7 4.6 VMF3-FC-G 3.5 2.4 5.9 1.8 1.7 4.1 VMF3-FC-S 3.6 2.4 6.0 1.7 1.7 4.1 春季 GPT3 2.5 1.9 5.9 1.6 1.3 5.2 VMF3-FC-G 2.5 1.9 5.4 1.6 1.4 4.6 VMF3-FC-S 2.5 1.9 5.4 1.6 1.3 4.4 夏季 GPT3 2.4 1.8 5.3 1.4 1.4 4.7 VMF3-FC-G 2.4 1.8 4.6 1.4 1.3 4.0 VMF3-FC-S 2.4 1.8 4.6 1.4 1.3 4.0 秋季 GPT3 2.6 1.8 5.0 1.5 1.3 4.4 VMF3-FC-G 2.6 1.8 4.8 1.5 1.3 4.1 VMF3-FC-S 2.6 1.8 4.8 1.5 1.2 4.1 平均 GPT3 2.8 2.0 5.7 1.5 1.4 4.7 VMF3-FC-G 2.8 2.0 5.2 1.6 1.4 4.2 VMF3-FC-S 2.8 2.0 5.2 1.5 1.4 4.2 表 4 3种映射函数BDS3和GPS PPP坐标外符合RMS/mm
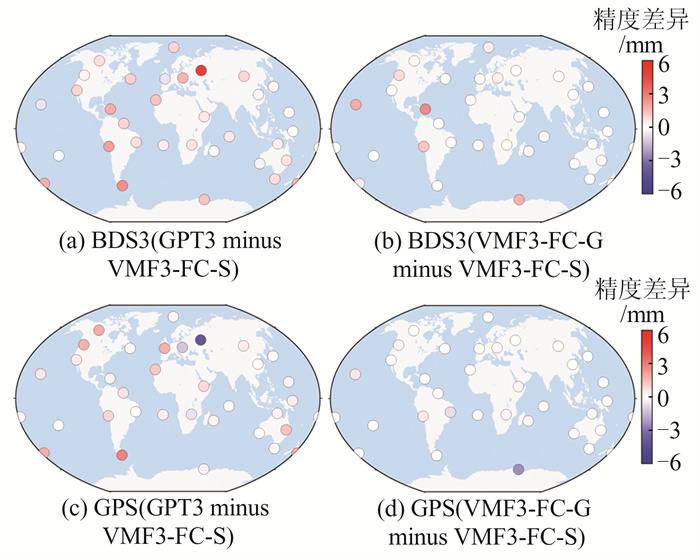
Table 4 Statistical BDS3 and GPS PPP Coordinate Cross-Validated RMS for the Three Mapping Functions/mm
模型产品 BDS3 RMS GPS RMS E N U E N U GPT3 5.5 4.0 10.5 2.6 2.9 6.3 VMF3-FC-G 5.5 4.0 10.2 2.6 2.9 5.8 VMF3-FC-S 5.4 3.9 9.8 2.6 2.9 5.9 表 5 3种映射函数BDS3和GPS PPP ZTD外符合RMS统计/mm
Table 5 Statistical BDS3 and GPS PPP ZTD Cross-Validated RMS for Three Mapping Functions/mm
模型产品 BDS3 RMS GPS RMS GPT3 8.5 7.4 VMF3-FC-G 8.6 7.4 VMF3-FC-S 8.6 7.4 -
[1] 章迪. GNSS对流层天顶延迟模型及映射函数研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017 Zhang Di. The Study of the GNSS Tropospheric Zenith Delay Model and Mapping Function[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2017
[2] 严豪健, 平劲松, 陈义, 等. 中性大气折射的映射函数[J]. 测绘学报, 1996, 25(1): 67-72 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.1996.01.011 Yan Haojian, Ping Jinsong, Chen Yi, et al. The Mapping Function of the Neutral Atmospheric Refraction[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 1996, 25(1): 67-72 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.1996.01.011
[3] 范昊鹏. 新一代大地测量VLBI关键技术及应用研究[D]. 郑州: 信息工程大学, 2018 Fan Haopeng. Research on Key Technologies and Applications of the New-Generation Geodetic VLBI [D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2018
[4] Niell A E. Global Mapping Functions for the Atmosphere Delay at Radio Wavelengths[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1996, 101 (B2): 3 227-3 246 doi: 10.1029/95JB03048
[5] Boehm J, Niell A, Tregoning P, et al. Global Mapping Function(GMF): A New Empirical Mapping Function Based on Numerical Weather Model Data [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(7): L07304 http://www.haystack.mit.edu/geo/pubs/gmf_2005GL025546.pdf
[6] Lagler K, Schindelegger M, Böhm J, et al. GPT2: Empirical Slant Delay Model for Radio Space Geodetic Techniques[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(6): 1 069-1 073 doi: 10.1002/grl.50288
[7] Boehm J, Werl B, Schuh H. Troposphere Mapping Functions for GPS and very Long Baseline Interferometry from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Operational Analysis Data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2006, 111(B2): B02406 doi: 10.1029/2005JB003629
[8] Boehm J, Kouba J, Schuh H. Forecast Vienna Mapping Functions 1 for Real-Time Analysis of Space Geodetic Observations[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2009, 83(5): 397-401 doi: 10.1007/s00190-008-0216-y
[9] 张双成, 叶世榕, 刘经南, 等. 动态映射函数最新进展及其在GNSS遥感水汽中的应用研究[J]. 武汉大学学报· 信息科学版, 2009, 34(3): 280-283 http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/1190 Zhang Shuangcheng, Ye Shirong, Liu Jingnan, et al. Latest Progress of Dynamic Mapping Functions and Its Application to GNSS Retrieved Water-Vapor [J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2009, 34(3): 280-283 http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/1190
[10] 郭际明, 章迪, 史俊波, 等. 利用射线追踪法分析三种典型对流层映射函数在中国区域的精度[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2015, 40(2): 182-187 http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/3182 Guo Jiming, Zhang Di, Shi Junbo, et al. Using Ray-Tracing to Analyse the Precision of Three Classical Tropospheric Mapping Functions in China[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(2): 182-187 http://ch.whu.edu.cn/article/id/3182
[11] 范昊鹏, 孙中苗, 张丽萍, 等. 顾及映射函数误差的对流层延迟两步估计法[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(3): 286-294 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201903004.htm Fan Haopeng, Sun Zhongmiao, Zhang Liping, et al. A Two-Step Estimation Method of Troposphere Delay with Consideration of Mapping Function Errors[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(3): 286-294 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201903004.htm
[12] 王朝阳, 卢勇夺, 邢喆, 等. 卫星截止高度角、对流层映射函数和海潮模型对南极GNSS精密定位的影响分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(12): 1 294-1 298 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB202012017.htm Wang Zhaoyang, Lu Yongduo, Xing Zhe, et al. Research on Influence of Satellite Cut-off Elevation Angle, Tropospheric Mapping Function and Ocean Tide Model on Antarctica GNSS PPP[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(12): 1 294- 1 298 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB202012017.htm
[13] Urquhart L, Nievinski F G, Santos M C. Assessment of Troposphere Mapping Functions Using Three-Dimensional Ray-Tracing[J]. GPS Solutions, 2014, 18(3): 345-354 doi: 10.1007/s10291-013-0334-8
[14] Kouba J. Testing of Global Pressure/Temperature (GPT) Model and Global Mapping Function (GMF)in GPS Analyses[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2009, 83(3/4): 199-208 http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jan_Kouba/publication/226357140_Testing_of_global_pressuretemperature_(GPT)_model_and_global_mapping_function_(GMF)_in_GPS_analyses._J_Geod_83(3-4)_199-208/links/54381e1d0cf204cab1d59e0f.pdf
[15] Steigenberger P, Boehm J, Tesmer V. Comparison of GMF/GPT with VMF1/ECMWF and Implications for Atmospheric Loading[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2009, 83(10): 943-951 doi: 10.1007/s00190-009-0311-8
[16] Yuan Y B, Holden L, Kealy A, et al. Assessment of Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 1 for RealTime Tropospheric Delay Modeling in GNSS[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2019, 93(9): 1 501-1 514 doi: 10.1007/s00190-019-01263-9
[17] Landskron D, Böhm J. VMF3/GPT3: Refined Discrete and Empirical Troposphere Mapping Functions [J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2018, 92(4): 349-360 doi: 10.1007/s00190-017-1066-2
[18] Saastamoinen J. Atmospheric Correction for the Troposphere and Stratosphere in Radio Ranging Satellites[M]//The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy. Washington D C: American Geophysical Union, 2013: 247-251
[19] Askne J, Nordius H. Estimation of Tropospheric Delay for Microwaves from Surface Weather Data [J]. Radio Science, 1987, 22(3): 379-386 doi: 10.1029/RS022i003p00379
[20] Zhou Y Z, Lou Y D, Zhang W X, et al. Improved Performance of ERA5 in Global Tropospheric Delay Retrieval[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(10): 1-14 doi: 10.1007/s00190-020-01422-3
[21] Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P, et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2020, 146(730): 1 999-2 049 doi: 10.1002/qj.3803
[22] Hofmeister A. Determination of Path Delays in the Atmosphere for Geodetic VLBI by Means of Raytracing[D]. Vienna: Technische Universität Wien, 2016
[23] Böhm J, Salstein D, Alizadeh M M, et al. Geodetic and Atmospheric Background[M]//Springer Atmospheric Sciences. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013: 1-33
[24] Wallace J M, Hobbs P V. Atmospheric Thermodynamics[M]//Atmospheric Science. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006: 63-111
[25] Rocken C, Sokolovskiy S, Johnson J M, et al. Improved Mapping of Tropospheric Delays[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2001, 18(7): 1 205-1 213 doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2001)018<1205:IMOTD>2.0.CO;2
[26] Nilsson T, Böhm J, Wijaya D D, et al. Path Delays in the Neutral Atmosphere[M]//Springer Atmospheric Sciences. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 73-136
[27] Rüeger J M. Refractive Index Formulae for Radio Waves[C]// The FIG XXⅡ International Congress, Washington D C, USA, 2002
[28] Boehm J. Troposphärische Laufzeitverzögerungen in der VLBI[D]. Vienna: Technische Universität Wien, 2004
[29] 魏二虎, 刘学习, 王凌轩, 等. BDS/GPS组合精密单点定位精度分析与评价[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2018, 43(11): 1 654- 1 660 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20160568 Wei Erhu, Liu Xuexi, Wang Lingxuan, et al. Analysis and Assessment of BDS/GPS Combined Precise Point Positioning Accuracy[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43 (11): 1 654-1 660 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20160568
[30] 崔浩猛, 王解先, 王明华, 等. 利用卫星分布概率对BDS-3性能的评估[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2021, 46(6): 938-946 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190172 Cui Haomeng, Wang Jiexian, Wang Minghua, et al. Service Performance Assessment of BDS3 Using Satellite Distribution Probability[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46 (6): 938-946 doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190172
[31] 张卫星. 中国区域融合地基GNSS等多种资料水汽反演、变化分析及应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2016 Zhang Weixing. Water Vapor Retrieval, Variation Analysis and Applications over China Using GroundBased GNSS and Multiple Data[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2016
[32] Bar-Sever Y E, Kroger P M, Borjesson J A. Estimating Horizontal Gradients of Tropospheric Path Delay with a Single GPS Receiver[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1998, 103 (B3): 5 019-5 035 doi: 10.1029/97JB03534
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陶叶青,束明聪,陈浩. 基于分类估计的异质数据融合M_(split)模型. 淮阴师范学院学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 45-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张双成,赵颖,张成龙,张菊清,樊茜佑,司锦钊,张雅斐,朱武,李振洪. 联合光学遥感和SAR影像青海玛多Ms 7.4地震同震形变场分析. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2025(03): 469-482 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 丁明涛,陈浩杰,李振洪,刘振江. 利用光学遥感影像光流场模型进行地表形变分析. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2024(08): 1314-1329 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载: