Phase Estimation for Inter-agency Interferometric Tracking in Chang'E-3 Powered Descent Flight
-
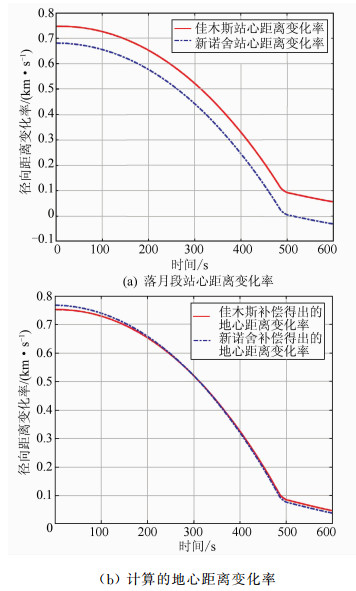
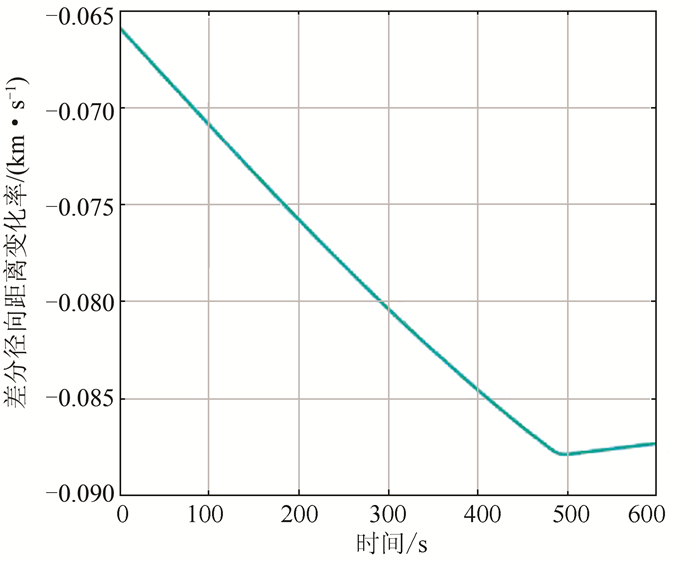
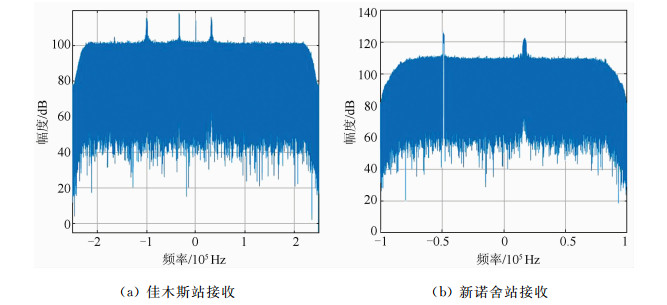
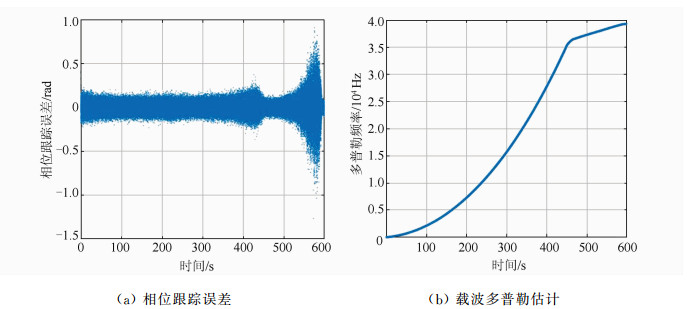
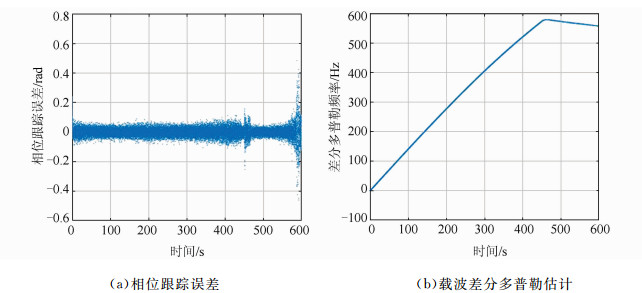
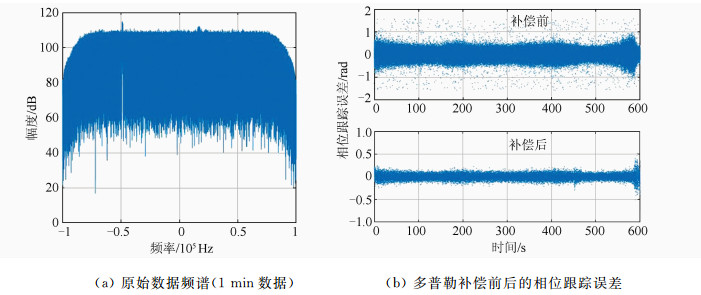
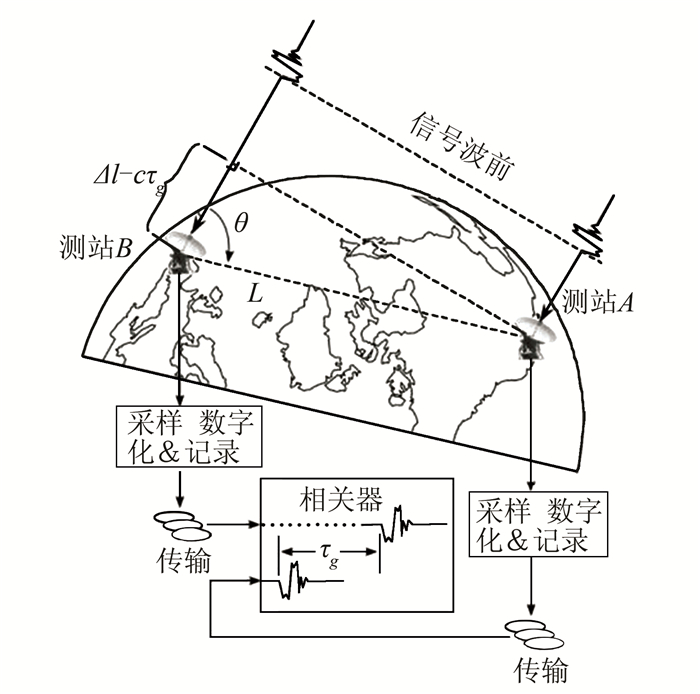
摘要: 干涉测量技术对于直接获取月球和深空探测器空间方位,开展科学研究具有非常重要的意义。提出了一种利用高品质因数天线获取的探测器高动态飞行段估计信息,对远距离异地较低接收品质因数天线接收的弱信号进行补偿,进而实现弱信号窄带跟踪的方法。利用嫦娥三号动力落月段中欧联合干涉测量获取的原始数据进行了验证,结果表明,基于该方法补偿后的弱信号只需采用噪声带宽5 Hz的数字锁相环即可实现精确相位跟踪,对新诺舍站DOR(differential one-way ranging)音信号的相位估计标准差低至3.4°。该方法可应用于中国未来月球和深空探测,以及机构间干涉测量交互支持。Abstract: Very long baseline interferometry plays a critical role on the orbit determination of the lunar and deep space probes, as well as the radio science research. Based on a first-order approximation model of the probe's topocentric range-rate, this paper proposes a new narrow band tracking method for the weak signal received by an antenna with relatively small aperture. As long as the Doppler dynamics has been estimated from the signal received by a large antenna with high G/T value, the weak signal, received by the small antenna during the same time duration, could be Doppler compensated. The raw data acquired by Chinese Jiamusi station and European Space Agency's New Norcia station have been processed, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of this method. Digital phase locked loop with 5 Hz noise bandwidth could be used to track the differential one-way ranging(DOR) tone received by New Norcia, after Doppler compensation by estimation results from Jiamusi carrier tracking, and the root mean square of the tracking phase errors for DOR tone is around 3.4 degree. This method could be used in the radio metric navigation for the future lunar and deep space missions, as well as the inter-agency cross-supports.
-
Keywords:
- moon exploration /
- power flight /
- weak signal /
- Doppler compensation /
- narrow band tracking
-
-
-
[1] 孙泽洲, 张廷新, 张熇, 等.嫦娥三号探测器的技术设计与成就[J].中国科学:技术科学, 2014, 44:331-343 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ce201404001 Sun Zezhou, Zhang Tingxin, Zhang Hao, et al. The Technical Design and Dchievements of Chang'E-3 Probe[J]. Sci Sin Tech, 2014, 44:331-343 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ce201404001
[2] Martin-Mur T J, Kruizinga G L, Burkhart P D, et al. Mars Science Laboratory Interplanetary Navigation[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2014, 51(4):1014-1028 doi: 10.2514/1.A32631
[3] Layland, Receiver J W. Design Concepts for VLBI and Differential One-Way Range[R]. DSN PR 42-50, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, US, 1979
[4] CCSDS 506.1-B-1, Delta-DOR Raw Data Exchange Format[S]. Blue Book, Space Communications and Navigation Office, Space Operation Mission Divectorate, NASA Headguart, Washington, D C, US, 2013
[5] CCSDS 500.1-G-1, Delta-DOR-Technical Characteristics and Performance[S]. Green Book, Space Communications and Navigation Office, Space Operation Mission Divectorate, NASA Headguart, Washington, D C, US, 2013
[6] Curkendall D W, Border J S. Delta-DOR: The One-Nanoradian Navigation Measurement System of the Deep Space Network-History, Architecture, and Compon-entry[R]. The Interplanetary Network Progress Report, Jet Propul-sion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, 2013
[7] Mercolino M, Ardito A, Barbaglio F, et al. A 1 nrad Delta-DOR System[C]. ESA International Workshop on Tracking, Telemetry and Command Systems for Space Applications, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2016
[8] Border J S. 210B Delta-Differential One Way Ranging[R]. DSMS Telecommunications Link Design Handbook, DSN No. 810-005, 210, Rev. B, JPL D-19379, CL#17-0718, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, US, 2017
[9] Vilnrotter V, Hamkins J, Ashrafi S. Performance Analysis of Digital Tracking Loops for Telemetry-Based Ranging Applications[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big SKy, Montana, US, 2014
[10] 谢钢. GPS原理与接收机设计[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2009 Xie Gang. Principles of GPS and Receiver Design[M]. Beijing:Publishing House of Electronic Industry, 2009
[11] Thornton C L, Border J S. Radiometric Tracking Techniques for Deep-Space Navigation[OL]. https://descanso.jpl.nasa.gov/monograph/series1/Descanso1_all.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 赵涛,叶世榕,罗歆琪,夏朋飞. GNSS-IR潮位反演中高仰角数据质量控制方法. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2024(01): 68-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 肖倩雨,周春霞,刘勇. 利用改进的亮温日较差法探测格陵兰冰盖表面融化. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2024(10): 1931-1939 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李荣兴,何美茜,葛绍仓,程远,安璐. 东南极历史冰流速过估改正. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2023(10): 1661-1669 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张冕,张春灌,赵敏,钟振华,袁炳强,周磊,韩梅. 地球磁异常EMAG2v3与全球重力数据库V29数据质量综合评估——以北极地区Aegir脊为例. 物探与化探. 2023(06): 1410-1416 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张金辉,李姗姗,杨光,范雕,凌晴. 联合CTD、海底地形和ARGO数据构建北太平洋深海时变温度模型. 测绘通报. 2023(12): 94-101+126 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 徐天河,穆大鹏,闫昊明,郭金运,尹鹏. 近20年海平面变化成因研究进展及挑战. 测绘学报. 2022(07): 1294-1305 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 徐天河,杨元元,穆大鹏,尹鹏. 近海海平面变化成因分析. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2022(10): 1750-1757 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈旭升,张云龙,张冠军. 优化局部均值分解在趋势信息提取中的应用. 测绘科学. 2022(11): 32-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 房婷婷,付广裕. 卫星重力与地球重力场的文献计量分析. 地球科学进展. 2021(05): 543-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 冯哲颖,岳林蔚,沈焕锋. 基于多源水文数据融合的GRACE水储量精度校正. 遥感技术与应用. 2021(03): 605-617 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘冰石,邹贤才. ENSO影响下的西太平洋地区海陆水储量变化分析. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2019(09): 1296-1303 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)





 下载:
下载: